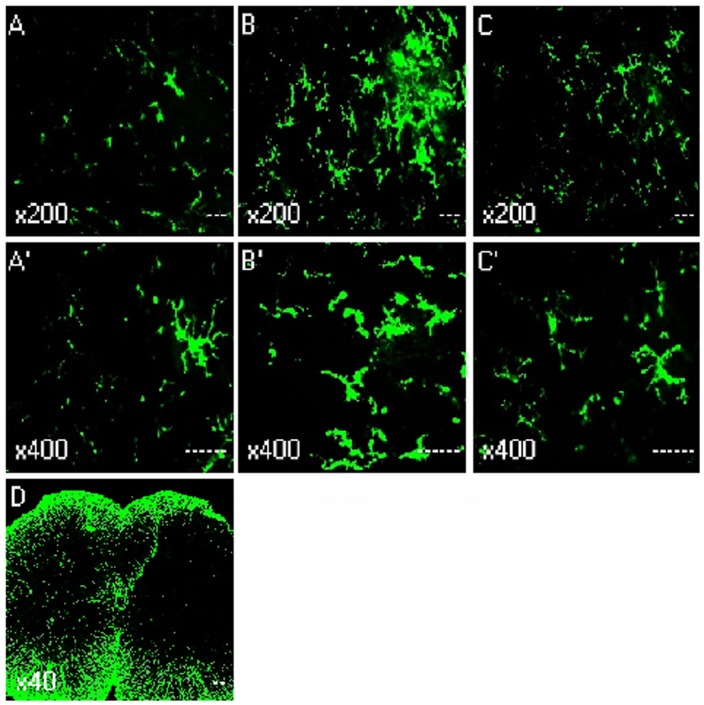
Figure 2. Immunohistochemistry showed the effects of intrathecal injection of spironolactone on activation of microglia in the spinal dorsal horn (n = 3/each).
Quantification of microglia activation after CCD surgery. Confocal images of sham (A and A’), Day 4 after CCD surgery (B, B’ and D), Day 4 after injection of spironolactone (C and C’), showing the increase in the microglia marker OX-42 in L4 spinal cord sections, the activated microglia cells typically exhibited hypertrophy with thicker processes, larger and densely stained cell bodies after CCD surgery. Injection of spironolactone inhibited microglia activation.