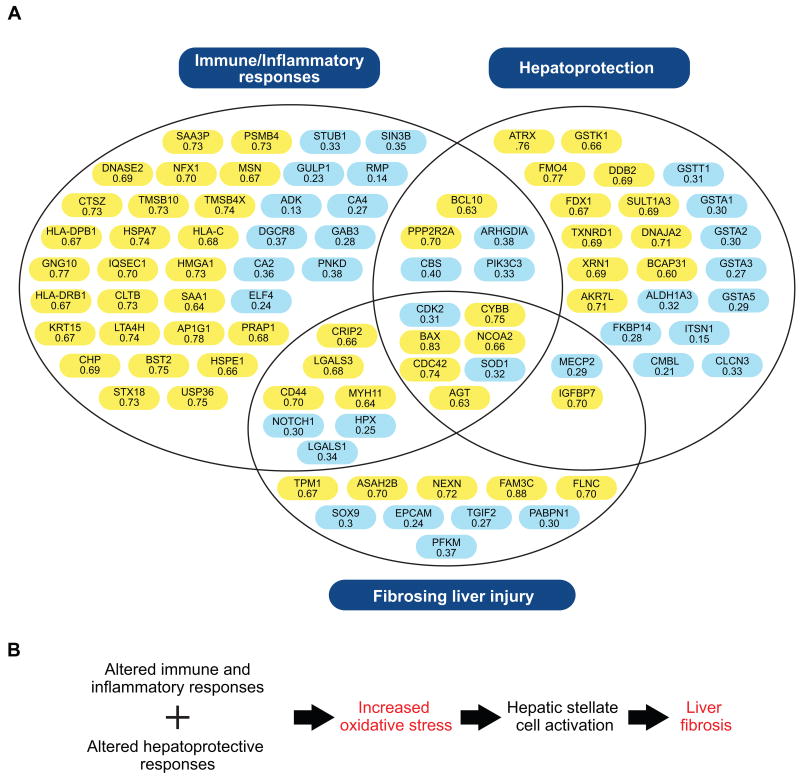
Figure 3. An overview of the differentially regulated proteins mapping to significant biological pathways and functions identified by IPA.
A) Proteins are organized within the generalized groupings immune/inflammatory response (i.e. the canonical pathways with higher expression in progressors), hepatoprotection (i.e. the canonical pathways with lower expression in progressors), and fibrosing liver injury (i.e. proteins associated with the toxicologic functional category of liver fibrosis). Proteins with AUC values > 0.6 were significantly up-regulated in rapid progressors both before and after histologic evidence of significant liver injury (highlighted in yellow) while those with AUC values < 0.4 were down-regulated (highlighted in blue). B) Molecular events in HCV-associated fibrogenesis. Patients with rapidly progressive liver disease exhibit altered immune/inflammatory responses and impaired anti-oxidant defenses, resulting in elevated oxidative stresses that promote liver fibrogenesis. The gene symbols and corresponding protein description are provided here. Additional information including the corresponding Swiss-Prot database accession number and EntrezGene identifier are also available in Table S4. ADK: adenosine kinase; AGT: pre-angiotensinogen; AKR7L: aldo-keto reductase family 7-like; ALDH1A3: aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A3; AP1G1: adaptor-related protein complex 1, gamma 1 subunit; ARHGDIA: Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha; ASAH2B: N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 2B; ATRX: alpha thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome X-linked; BAX: BCL2-associated X protein; BCAP31: B-cell receptor-associated protein 31; BCL10: B-cell CLL/lymphoma 10; BST2: bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2; CA2: carbonic anhydrase 2; CA4: carbonic anhydrase 4; CBS: cystathionine beta synthase; CD44: CD44 antigen (Indian blood group); CDC42: cell division cycle 42 (GTP binding protein, 25kDa); CDK2: cyclin-dependent kinase 2; CHP: calcium-binding protein P22; CLCN3: chloride channel 3; CLTB: clathrin, light chain B; CMBL: carboxymethylenebutenolidase homolog; CRIP2: cysteine-rich protein 2; CTSZ: cathepsin Z; CYBB: cytochrome b-245 beta; DDB2: damage-specific DNA binding protein 2, 48kDa; DGCR8: DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8; DNAJA2: DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily A, member 2; DNASE2: deoxyribonuclease II, lysosomal; ELF4: E74-like factor 4 (ets domain transcription factor); EPCAM: epithelial cell adhesion molecule; FAM3C: family with sequence similarity 3, member C; FDX1: ferredoxin 1; FKBP14: FK506 binding protein 14; FLNC: filamin C, gamma; FMO4: flavin containing monooxygenase 4; GAB3: GRB2-associated-binding protein 3; GNG10: guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma; GSTA1: glutathione S-transferase alpha 1; GSTA2: glutathione S-transferase alpha 2; GSTA3: glutathione S-transferase alpha 3; GSTA5: glutathione S-transferase alpha 5; GSTK1: glutathione S-transferase kappa 1; GSTT1: glutathione S-transferase theta 1; GULP1: GULP, engulfment adaptor PTB domain containing 1; HLA-C: major histocompatibility class I antigen C; HLA-DPB1: major histocompatibility class 2 antigen DP beta 1; HLA-DRB1: major histocompatibility class 2 antigen DR beta 1; HMGA1 high mobility group AT-hook 1; HPX: hemopexin; HSPA7: heat shock 70kDa protein 7 (HSP70B); HSPE1: heat shock 10kDa protein 1 (chaperonin 10); IGFBP7: insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7; ITSN1: intersectin 1; IQSEC1: IQ motif and Sec7 domain 1; KRT15: keratin 15; LGALS1: galectin 1; LGALS3: galectin 3; LTA4H: leukotriene A4 hydrolase; MECP2: methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (Rett syndrome); MSN: moesin; MYH11: myosin, heavy chain 11, smooth muscle; NCOA2: nuclear receptor coactivator 2; NEXN: nexilin; NFX1: nuclear transcription factor, X-box binding 1; NOTCH1: notch 1; PABPN1: polyadenylate-binding protein, nuclear 1; PFKM: phosphofructokinase, muscle; PIK3C3: phosphoinositide-3-kinase, class 3; PNKD: paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia; PPP2R2A: protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit B, alpha; PSMB4: proteasome beta subunit type 4; PRAP1: proline-rich acidic protein 1; RMP: RNA polymerase II, subunit 5-mediating protein; SAA1: serum amyloid A1; SAA3P: putative serum amyloid A-3 protein; SIN3B: SIN3 homolog B, transcription regulator (yeast); SOD1: superoxide dismutase 1; SOX9: SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9; SULT1A3: aryl sulfotransferase 1A3; STUB1: STIP1 homology and U box-containing protein 1; STX18: syntaxin-18; TGIF2: TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2; TMSB10: thymosin beta-10; TMSB4X: thymosin beta-4; TPM1: tropomyosin 1 (alpha); TXNRD1: thioredoxin reductase 1; USP36: ubiquitin specific peptidase 36; XRN1: 5′-3′ exoribonuclease 1.