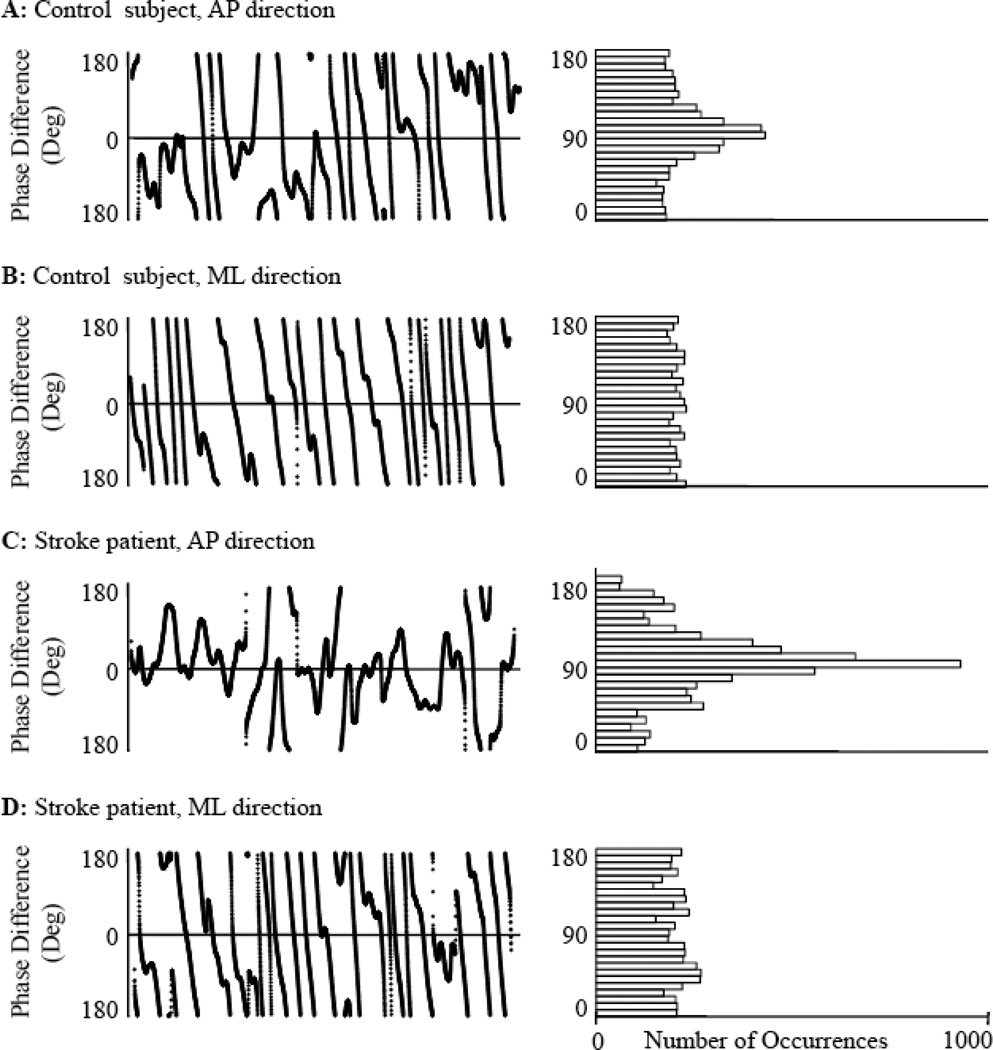
Figure 2. Instantaneous phase differences between respiratory flow and center-of-pressure dynamics during quiet standing with eyes open for a control and a stroke subject.
Phase differences (left panels) were calculated between the dominant oscillatory mode of respiratory flow and the corresponding modes of anterioposterior (AP) and mediolateral (ML) center-of-pressure fluctuations for a representative control (A-B) and stroke subject (C-D). Corresponding distributions of instantaneous phase differences are shown in the right panels. Compared to the ML direction for both subjects, the phase differences in the AP direction were more normally distributed from −180 to 180 degrees. Thus, Shannon entropy was smaller and the phase synchronization index was larger (i.e., stronger synchronization) in the AP direction.