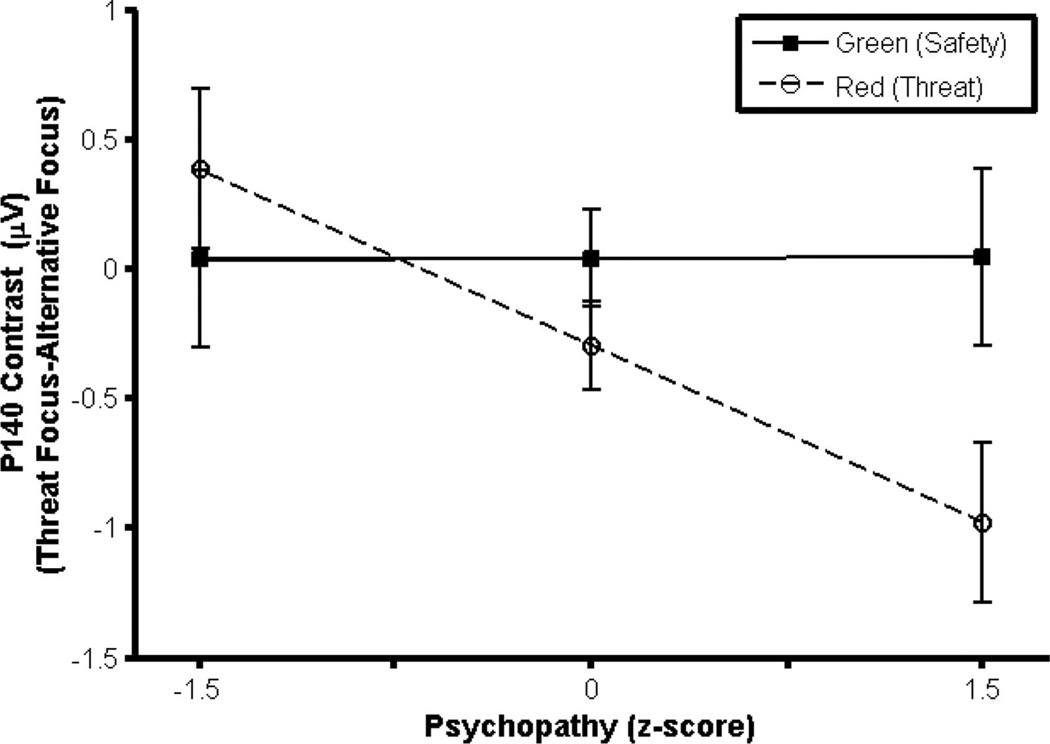
Figure 2.
P140 and psychopathy. The relationship between psychopathy and P140 was moderated by threat and focus of attention (Psychopathy × Threat × Attentional focus interaction contrast). Average P140 magnitude was calculated as the mean across midline sites. Using points estimates generated from the GLM, the P140 means for the interaction contrast (attentional manipulation) in the red and green trials displayed for psychopathy were calculated at 1.5 SD below and above the sample mean on psychopathy total scores, respectively. Error bars represent the standard error for the point estimates. The relationship between psychopathy and P140 was moderated by color and focus of attention. There was no psychopathy-related difference in green (no threat) letters, but there was a significant difference in red (threat) letters. Individuals high on psychopathy (+1.5) showed greater P140 to red (threat) letters in alternative-focus versus threat-focus conditions.