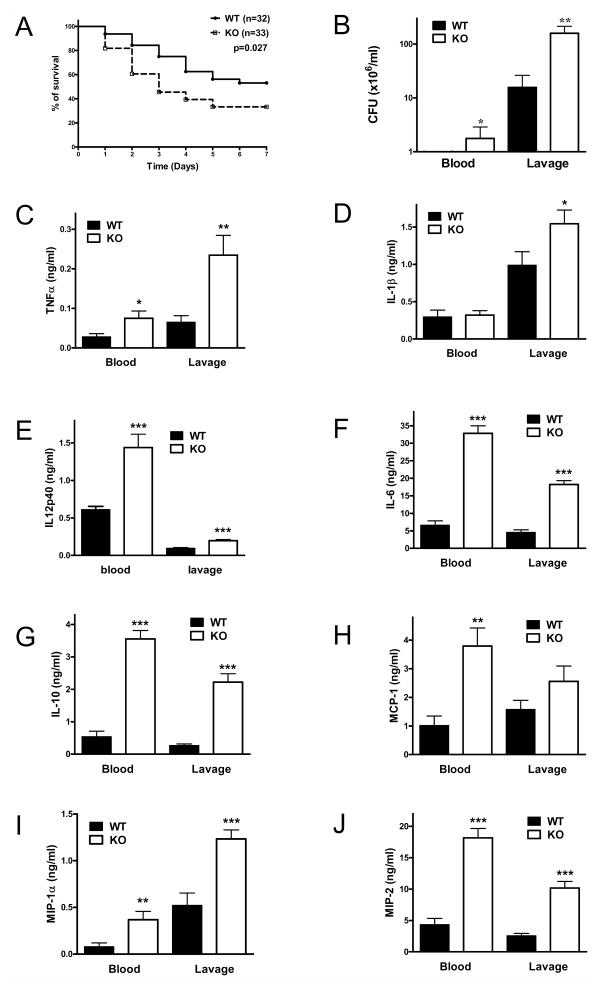
Figure 1. Loss of CD73 decreases survival, and increases bacterial load and inflammation in polymicrobial sepsis.
(A) The number of surviving CD73 WT and KO mice were counted daily for 7 days after inducing sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). (B) Blood and peritoneal lavage fluid obtained from CD73 WT and KO mice 16 h post CLP were cultured on soy-trypticase agar plates for 24 h and then the bacterial colonies were counted (n = 13 mice per group). Serum and peritoneal lavage fluid concentration of TNF-α (C), IL-1β (D), IL12p40 (E), IL-6 (F), IL-10 (G), MCP-1 (H), MIP-1α (I) and MIP-2 (J) were determined in samples collected 16 h post CLP using ELISA. All results (mean ± SEM) shown are representative of three separate experiments. * p < 0.05 versus WT; ** p < 0.01 versus WT; * ** p < 0.001 versus WT.