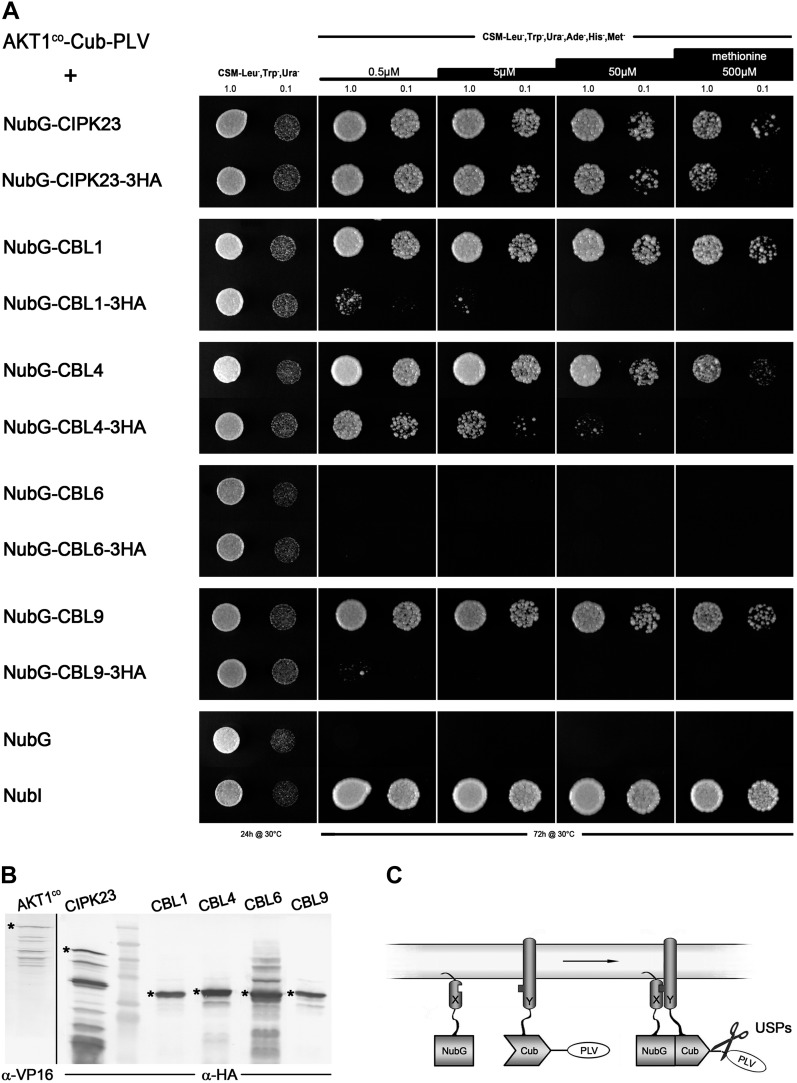
Figure 2.
SUS analysis of full-length AKT1 with CIPK23 and exemplary CBL proteins. A, Growth assay of diploid yeast containing a Met-repressible bait construct, AKT1co-Cub-PLV, and different prey constructs. CBL and CIPK23 proteins were either N-terminally tagged (NubG; each top row) or N- and C-terminally tagged (NubG at the N terminus and triple-HA tag at the C terminus; each bottom row). Yeast were dropped at optical density values of 1.0 and 0.1 on vector-selective (CSM-Leu-,Trp-,Ura-) and interaction-selective (CSM-Leu-,Trp-,Ura-,Ade-,His-,Met-) media with increasing Met concentrations. Growth was monitored after 24 h for the vector-selective control plates and after 72 h for the actual interaction plates. As negative and positive controls, AKT1co-Cub-PLV-expressing yeast were mated with yeast containing only NubG or NubI (wild-type Nub) peptides. B, Western-blot analyses of all haploid yeast clones prior to mating, verifying the expression of both bait and prey (C-terminally HA-tagged) fusions. Asterisks mark the bands that correspond to the expected protein sizes of the respective fusion proteins: AKT1co-Cub-PLV = 150.5 kD; NubG-CIPK23-3xHA = 63.7 kD; NubG-CBL1-3xHA = 34.8 kD; NubG-CBL4-3xHA = 35.9 kD; NubG-CBL6-3xHA = 36.3 kD; NubG-CBL9-3xHA = 34.8 kD. C, Schematic depiction of the SUS assay demonstrating the cleavage of the PLV transcription factor construct upon reassembly of the ubiquitin halves. PLV, Protein A-LexA-VP16.