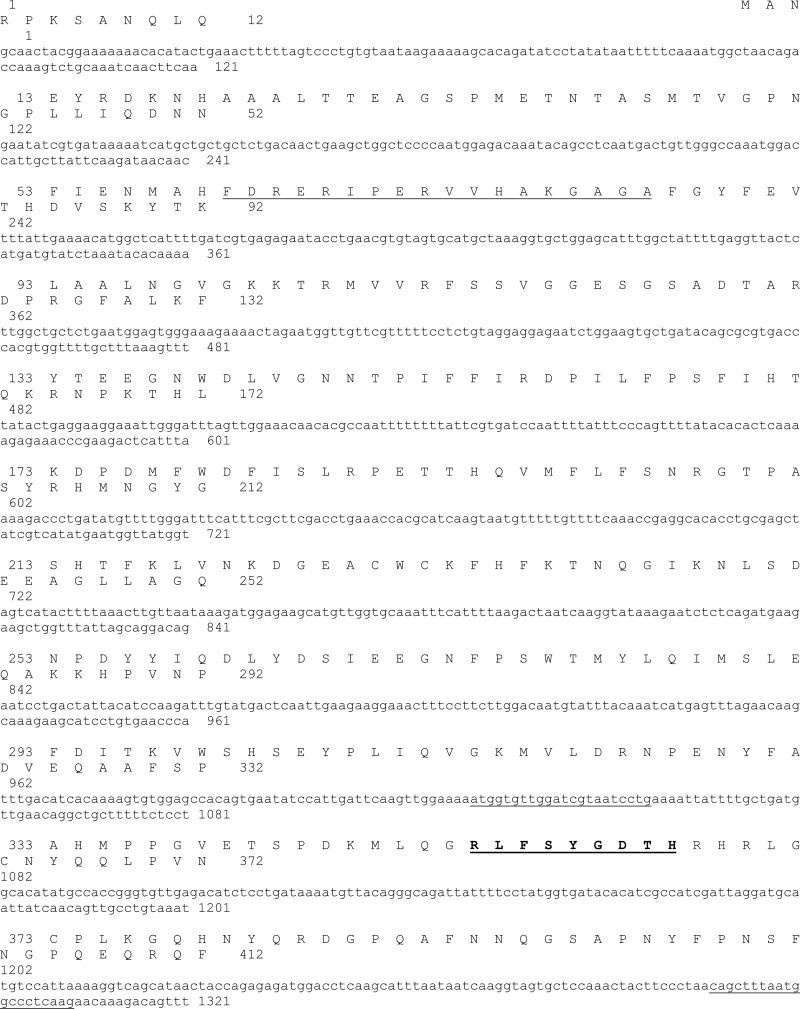
Fig.1.
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of H. vulgaris monofunctional catalase cDNA. The deduced amino acid sequence is shown in single-letter code above the nucleotide sequence. The nucleotide and amino acid sequences are numbered from the 5’-end of the 1859 bp cDNA sequence, and from the N-terminal start codon methionine, respectively. The asterisk denotes the translation stop signal. Underlined nucleotide sequences indicate primer positions and/sequences for the initial cloning of an HvCatalase cDNA fragment. Putative proximal active site signature is underlined and the proximal heme ligand signature is bold and underlined. Putative amino acid residues in bold letter with light gray shade indicate putative NADPH binding residues in reference to H. sapiens catalase (Putnam et al., 2000).