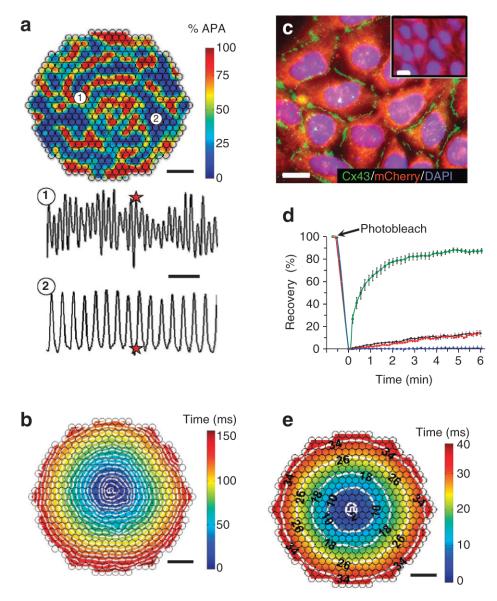
Figure 3. Stable overexpression of Cx43 in Kir2.1 + Nav1.5 HEK-293 cells yields enhanced intercellular coupling and permits rapid AP propagation.
(a) At the start of recording, confluent isotropic 2D networks (monolayers) of monoclonal Kir2.1 + nav1.5 cells usually exhibited high-frequency unorganized electrical activity caused by numerous, slowly moving, splitting and colliding waves. shown is one instant of optically recorded transmembrane voltage. Colour bar indicates percent AP amplitude (% APA). Different sites in the monolayer (for example, 1 and 2) activated at different rates (bottom panel), demonstrating the lack of spatial synchrony in activation. Red stars denote the time at which the transmembrane voltage frame (top panel) was taken. scale bars indicate 3 mm (top panel) and 250 ms (bottom panel). (b) on successful termination of all unorganized activity by a strong field shock, low-frequency ( < 10 Hz) point stimulation from the centre (white pulse sign) yielded slow conduction through the weakly coupled Kir2.1 + nav1.5 HEK-293 cells. shown is a colour-coded map of cell activation, with white isochrone lines drawn at every 8 ms. scale bar, 3 mm. (c) Following stable Cx43 overexpression, the derived Kir2.1 + nav1.5 + Cx43 HEK-293 cells formed abundant intercellular Cx43 gap junctions (green), which were not detected in wt HEK-293 cells (inset). scale bars, 10 μm. (d) Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching shows increased functional coupling in monoclonal Kir2.1 + nav1.5 + Cx43 (Ex-293) cells (green squares; n = 7) compared with wt HEK-293 (black diamonds; n = 6) and Kir2.1 + nav1.5 HEK-293 (red triangles; n = 5) cells. Palmitoleic acid (PA) inhibited junctional coupling and fluorescence recovery (blue circles; n = 6). Error bars denote s.e.m. (e) Pacing in the centre of an Ex-293 monolayer elicited rapid and uniform AP spread (see supplementary movie 1). scale bar, 3 mm. Isochrones of cell activation (white lines) are labelled in milliseconds. small black circles in a, b, and e denote 504 optical recording sites. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.