Figure 2.
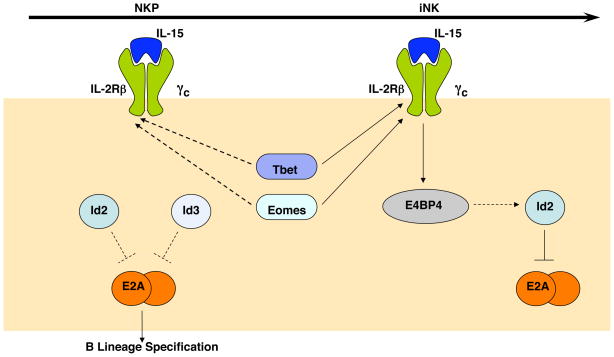
Transcription Factors in Early Natural Killer Cell Development. At the present time there are only a few transcription factors that are known to play a role in NK cell development. Within NKPs Id2 and Id3 are thought to function redundantly to repress E2A and prevent activation of the B lymphocyte gene program, although this hypothesis remains to be tested. T-bet and Eomes are expressed in NKPs and are likely required for expression of CD122, the β-chain of the IL15 receptor, as they are known to do in iNK cells. IL15 is essential at the iNK cell stage and activates the bZIP transcription factor E4BP4 (also known as Nfil3), which has been implicated in the up-regulation of Id2. At the iNK cell stage Id3 is down-regulated and Id2 is essential for repression of E2A.