Figure 4.
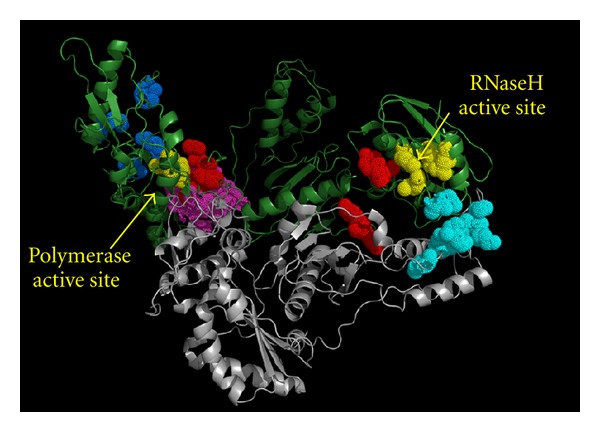
Amino acid residues involved in RTI binding. RT two subunits are in green (p66) and in gray (p51). The catalytic residues of the polymerase active site and the RNase H active site are colored in yellow. NRTIs and NtRTIs interact with residues close to the polymerase active site (blue). NNRTIs bind in a hydrophobic pocket next to the polymerase active site (magenta). RHRTIs such as DKAs, N-hydroxyimides, N-hydroxy quinazolinediones and naphthyridine derivatives bind in the RNase H active site (in yellow on the right). Vinylogous ureas bind to a hydrophobic pocket at the interface between the RNase H domain and the p51 subunit (cyan). Hydrazone derivatives have been proposed to bind two different sites (red). One located between the polymerase active site and the NNRTI-binding pocket (sharing a few residues with it) and the second one located between the RNase H and the connection domain. Anthraquinone derivatives have been proposed to bind to the first hydrazone pocket next to the NNRTI-binding site.
