Figure 2.
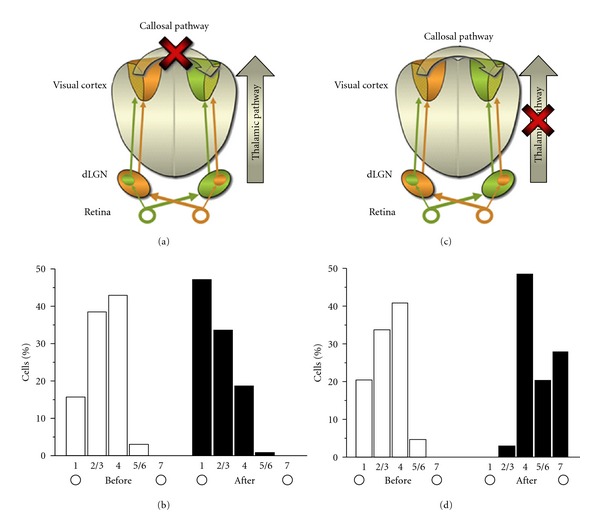
Relative contribution of callosal and thalamic pathways to cortical binocularity. (a, b) Effects of acute callosal silencing on OD in rat primary visual cortex. Binocularity was measured in one side before and after acute pharmacological inactivation of the opposite cortex (a). The results indicate a significant shift of cortical OD towards the contralateral eye, due to the reduction of responses driven by the ipsilateral eye (b). (c, d) Effects of acute geniculate silencing on OD in rat primary visual cortex. The OD histogram shifts towards the ipsilateral eye following acute geniculate inactivation (d). This effect is mainly due to a loss of contralateral eye-driven input. Data are from [32, 55].
