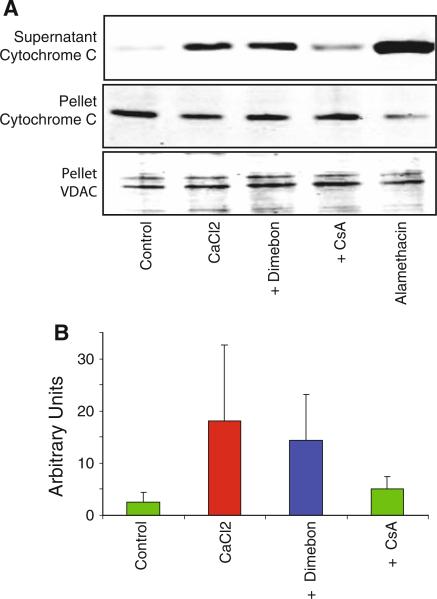
Fig. 3.
Dimebon does not alter calcium-induced cytochrome c release from rat brain mitochondria. Non-synaptic mitochondria from rat brain were incubated in 250 μM CaCl2 for 30 min, then centrifuged and cytochrome C evaluated in the supernatant and pellet by western blotting. Dimebon (200 μM) or cyclosporin A (CsA, 5 μM) was added to the incubation media. The voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), a mitochondrial protein, was monitored as a loading control. Alamethacin was used to induce maximal cytochrome C release for comparison with CaCl2. a Representative western blots of the pellet and supernatant fractions. b Quantitative results from four animals in each group (mean ± SD). The results demonstrated calcium-induced cytochrome C release from rat brain mitochondria but that Dimebon did not influence the extent of cytochrome C release, in contrast to CsA