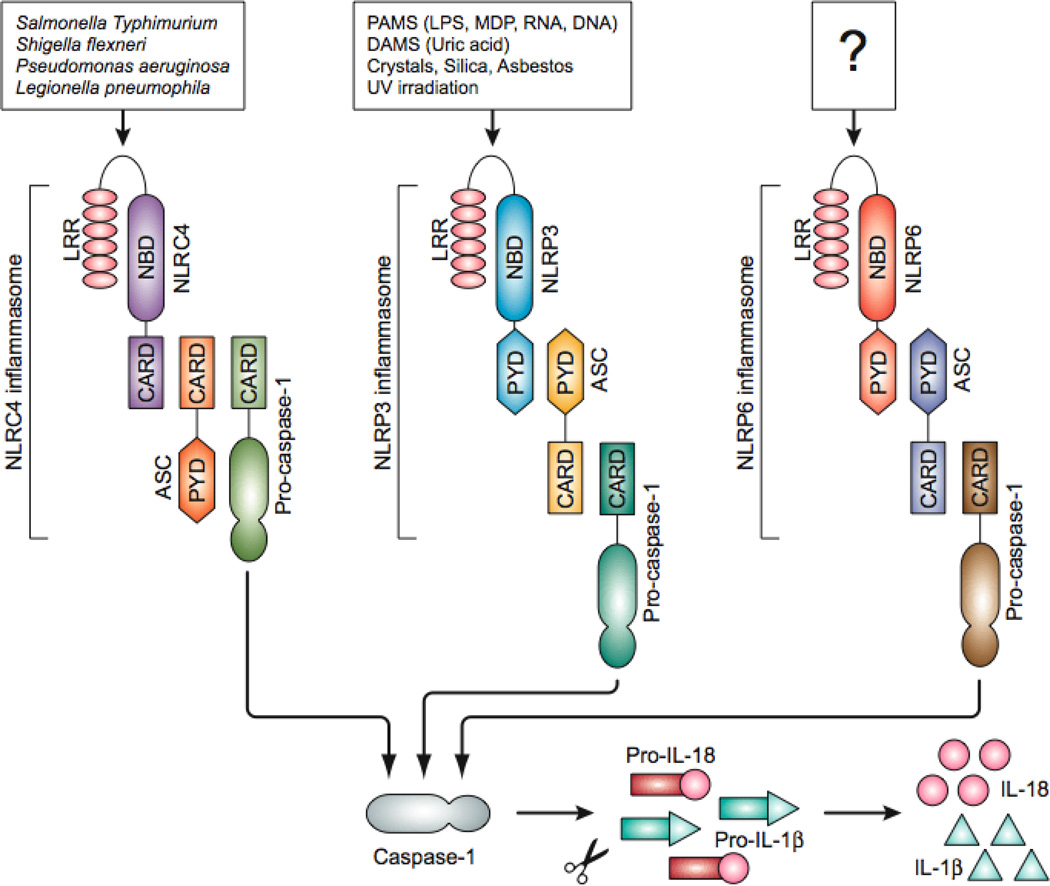
Figure 1. Inflammasomes involved in intestinal inflammation.
Three different inflammasome complexes consists of NOD-like receptors (NLR) - NLRC4, NLRP3, and NLRP6 - have been known to be involved in colitis and colorectal tumorigenesis. The NLRC4 inflammasome senses the cytosolic presence of several Gram-negative bacteria including S. typhimurium, S. Flexneri, L. pneumophila and P. aeruginosa. The NLRP3 is activated by microbial PAMPs such as LPS, MDP and bacterial RNA, endogenous DAMPs such as ATP, crystals such as monosodium urate, silica and asbestos, or UV irradiation. How the other inflammasome, NLRP6, is activated is still unknown. Once the NLRs are activated they form the inflammasome complex with caspase-1 via adaptor protein ASC. Activated caspase-1 processes the IL-1β and IL-18 precursors into the mature cytokines, which are secreted through an unknown mechanism. CARD, caspase recruitment domain; PYD, pyrin domain; NBD, nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain; LRR, leucine rich repeat; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; DAMS, danger-associated molecular patterns.