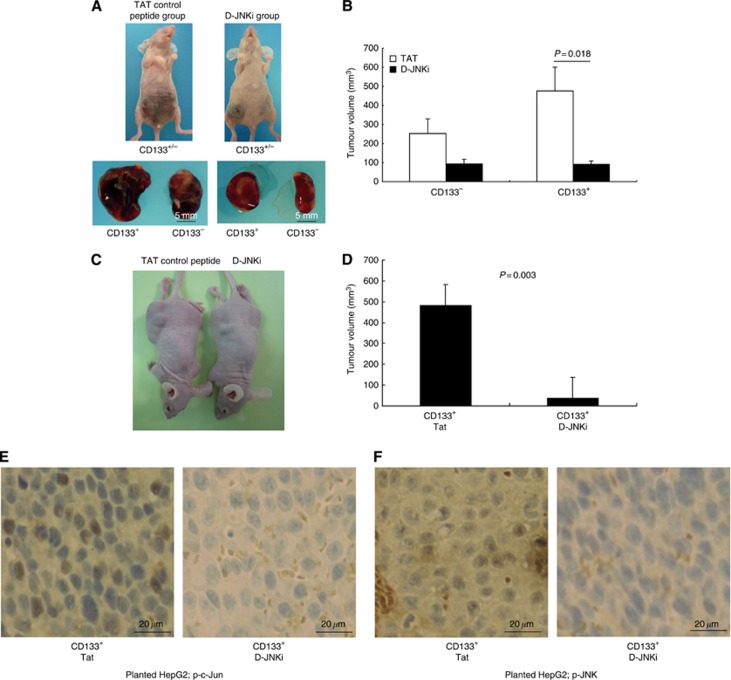
Figure 5.
Effect of a JNK inhibitor on tumourigenic potential of CD133+ HCC cells. (A) HepG2 cells positive or negative for CD133 were inoculated subcutaneously at 8 × 104 cells per body into nude mice (n=8). From 1 week after subcutaneous inoculation, TAT control peptide and D-JNKi, a specific JNK inhibitor, were administered at 25 nmol per mouse once a week and the mice were autopsied 4 weeks later. Representative nude mice with subcutaneous tumours derived from CD133+ (left) and CD133− (right) HepG2 cells. (B) Tumourigenicity of CD133+ or CD133− HepG2 cells treated with D-JNKi or control Tat protein. (C) HuH7 cells positive for CD133 were inoculated subcutaneously at 1 × 106 cells per body into nude mice (n=6). From 1 week after subcutaneous inoculation, TAT control peptide and D-JNKi were administered at 25 nmol per mouse once a week and the mice were autopsied 4 weeks later. Representative nude mice with subcutaneous tumours were shown. (D) Tumourigenicity of CD133+ HuH7 cells treated with D-JNKi or control Tat protein. (E) Expression of phospho-c-Jun in xenografted tumours treated with D-JNKi or control protein. (F) Expression of phospho-JNK in xenografted tumours treated with D-JNKi or control protein.