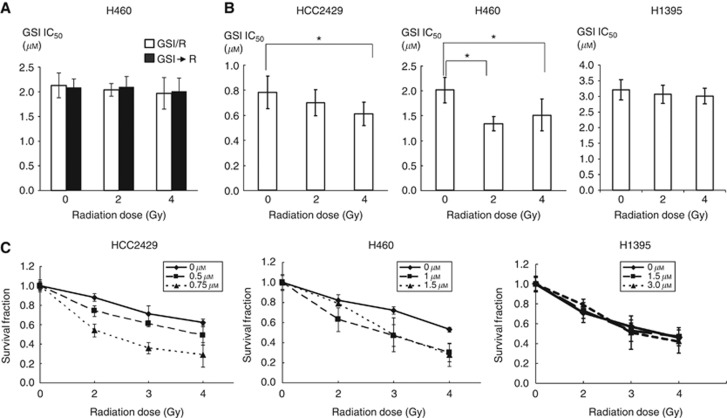
Figure 1.
GSI after radiation suppressed proliferation of lung cancer. (A) Comparison of IC50 values in the different treatment schedule in the MTT proliferation assay. Neither concurrent treatment schedule nor radiation after GSI I administration had a significant impact on tumour proliferation compared with GSI I alone (0 Gy). Plated cells were treated with GSI I and radiation simultaneously or radiation at 24 h after GSI I administration (n=5). Treated cells were incubated for 8 days. GSI/R: concurrent treatment schedule. GSI→R: radiation after GSI I administration. (B) Comparison of IC50 in GSI I after radiation. Plated cells were treated with GSI I at varying doses at 24 h after radiation. IC50 was less for combined therapy than for GSI I alone in both HCC2429 and H460 cell lines (n=5). *P<0.05. On the contrary, IC50 was not different between GSI alone and combination in H1395. (C) GSI I after radiation decreased clonogenic survival in HCC2429 and H460, but not in H1395 (n=3). Cells were plated overnight and then exposed to radiation with 0 to 4 Gy as indicated. GSI I at varying doses was added at 24 h after radiation and then cells were incubated for 8 days.