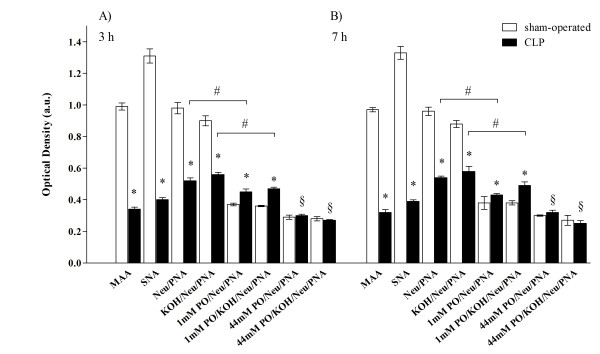
Figure 5.
Sepsis was associated with reduced expression and changes in chemical structure of GFB sialic acids. Quantitative analysis of lectin histochemistry at 3 and 7 hours after sham or CLP operation. Reactivity intensity of MAA, SNA and PNA, after treatment with neuraminidase (with and without deacetylation), was significantly lower in CLP compared to sham-operated samples, demonstrating a decrease of sialic acid in septic rats. After mild oxidation-neuraminidase treatment (with and without deacetylation), PNA reactivity intensity was lower in sham-operated than in CLP rats, demonstrating a major amount of sialic acid with acetylic groups in C7- and/or C8- and/or C9- in septic rats. Data from mild oxidation were lower compared to those without mild oxidation for both sham-operated and CLP rats, indicating that some but not all sialic acids were acetylated in C7-and/or C8- and/or C9-. No significant difference between groups was observable in PNA reactivity intensity, after strong oxidation-neuraminidase treatment, with and without deacetylation; for both groups, reactivity intensity was statistically lower when compared to the neuraminidase PNA reactivity with and without mild oxidation, thus indicating that some sialic acids were acetylated in C9 and linked α-2,3. No difference between 3 and 7 hours was found. (* P <0.05 sham-operated versus CLP same reaction; # P <0.05 mild oxidation versus without oxidation; § P <0.05 strong versus mild and versus without oxidation, panels A and B). CLP, cecal ligation and puncture; MAA, Maackia amurensis agglutinin; PNA, peanut agglutinin (Arachis hypogaea); SNA, Sambucus nigra agglutinin; Neu/PNA, neuraminidase/PNA; KOH/Neu/PNA, deacetylation/neuraminidase/PNA; 1 mM PO/Neu/PNA, mild oxidation/neuraminidase/PNA; 1 mM PO/KOH/Neu/PNA, mild oxidation/deacetylation/neuraminidase/PNA; 44 mM PO/Neu/PNA, strong oxidation/neuraminidase/PNA; 44 mM PO/KOH/Neu/PNA, strong oxidation/deacetylation/neuraminidase/PNA.