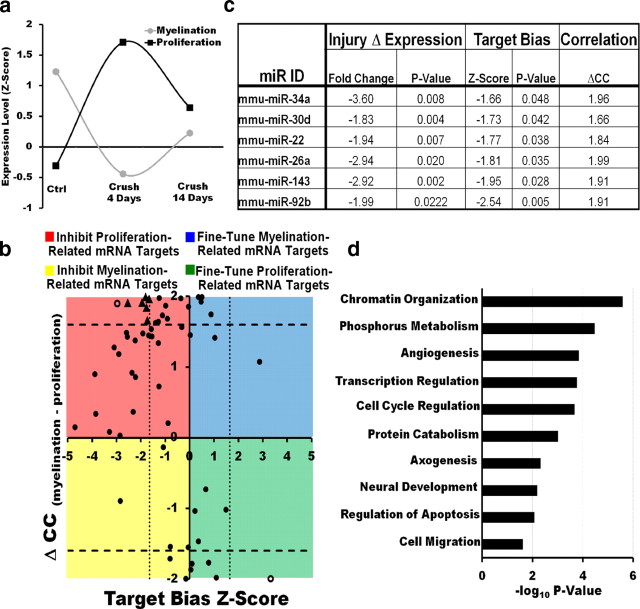
Figure 2.
Target bias analysis suggests that SC miRNAs modulate the injury response by repressing positive regulators of SC dedifferentiation/proliferation. a, mRNA expression profiles of gene clusters containing known regulators of SC dedifferentiation/proliferation (the proliferation profile) or differentiation/myelination (the myelination profile) after injury. b, Graph plotting the target bias for each miRNA in subset 1 (measured by a Mann–Whitney z-score) against the correlation of its expression with the myelination or proliferation profile (measured by ΔCC, the difference in correlation coefficients with the proliferation profile and the myelination profile). Biological functions of miRNAs in regulating the SC injury response may be inferred from their correlation with the proliferation or myelination gene clusters and by their positive or negative target bias. The majority of SC miRNAs cluster in the top left quadrant of the graph (negative target bias, correlation with the myelination profile), suggesting that SC miRNAs are likely to modulate the injury response primarily through their inhibition of positive regulators of SC dedifferentiation/proliferation. Dotted and dashed lines represent statistical significance cutoffs. miRNAs differentially regulated after injury (C4 vs Ctrl p < 0.05), with a statistically significant target bias and a high correlation with the myelination or proliferation clusters (ΔCC > 1.6), are represented by triangles. Empty circles represent miRNAs that met statistical significance cutoffs for target bias and high correlation with the myelination or proliferation clusters, but were not differentially regulated after injury. c, miRNAs likely to be direct regulators of the SC injury response (triangles in b) based on their differential regulation after injury, significant target bias, and a high correlation with the myelination or proliferation clusters. d, Predicted targets for miRNAs in c are enriched for genes involved in cellular processes that are normally inhibited in adult or differentiating SCs but are active in immature or proliferating SCs.