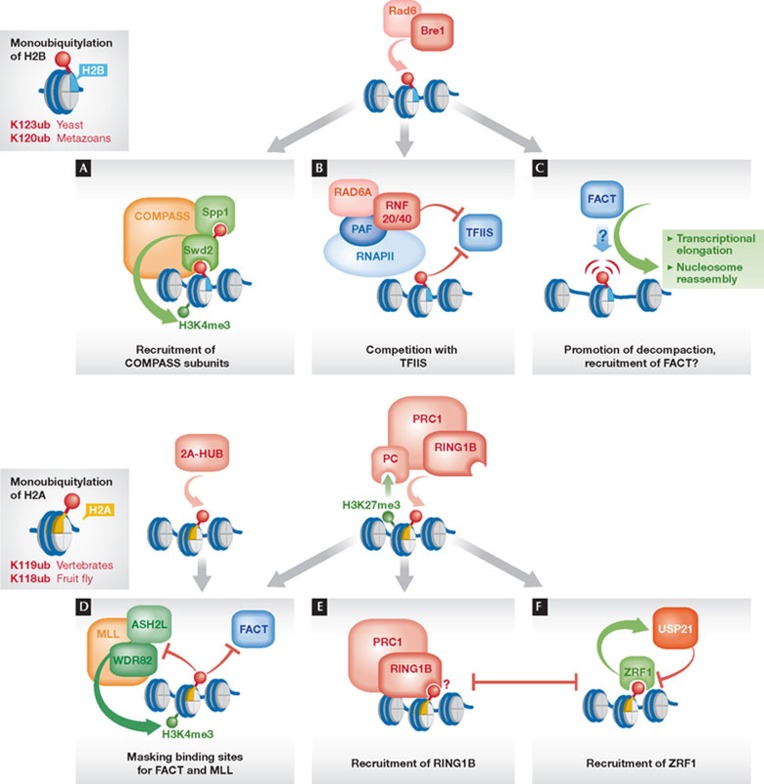
Figure 2. Shaping of chromatin through monoubiquitylation of histones H2B and H2A.
(A) H2Bub mediates recruitment of the COMPASS subunit Swd2 required for trimethylation of H3K4. Swd2 itself is ubiquitylated in a manner dependent on Rad6–Bre1, which mediates the association with Spp1, another COMPASS subunit involved in H3K4 trimethylation. (B) RNF20 and H2Bub negatively regulate chromatin recruitment of TFIIS. (C) H2Bub mediates structural changes by interfering with chromatin compaction, thereby facilitating the association of FACT to chromatin. (D) Ubiquitylation of H2A by the E3s 2A-HUB and RING1B negatively regulates the function or recruitment of the mammalian HMTase complex MLL and FACT. (E) H2Aub mediates binding of PRC1 to chromatin, possibly through direct recognition by RING1B. (F) H2Aub mediates the recruitment of ZRF1, which competes with PRC1 for binding to chromatin and facilitates the binding and/or function of the H2A deubiquitylase USP21. COMPASS, complex proteins associated with Set1, H3K4 HTMase complex; FACT, facilitates chromatin transcription, heterodimeric histone chaperone; H2Bub, H2B ubiquitylation; HMTase, histone methyltransferase; K, lysine (Lys); MLL, mixed leukaemia lineage complex, mammalian H3K4 HMTase; PAF, polymerase II association factor; PC, Polycomb; PRC1, Polycomb repressor complex 1; RING1B, really interesting new gene 1B; TFIIS, transcription factor IIS; USP21, ubiquitin-specific protease 21; ZRF1, zuotin-related factor 1.