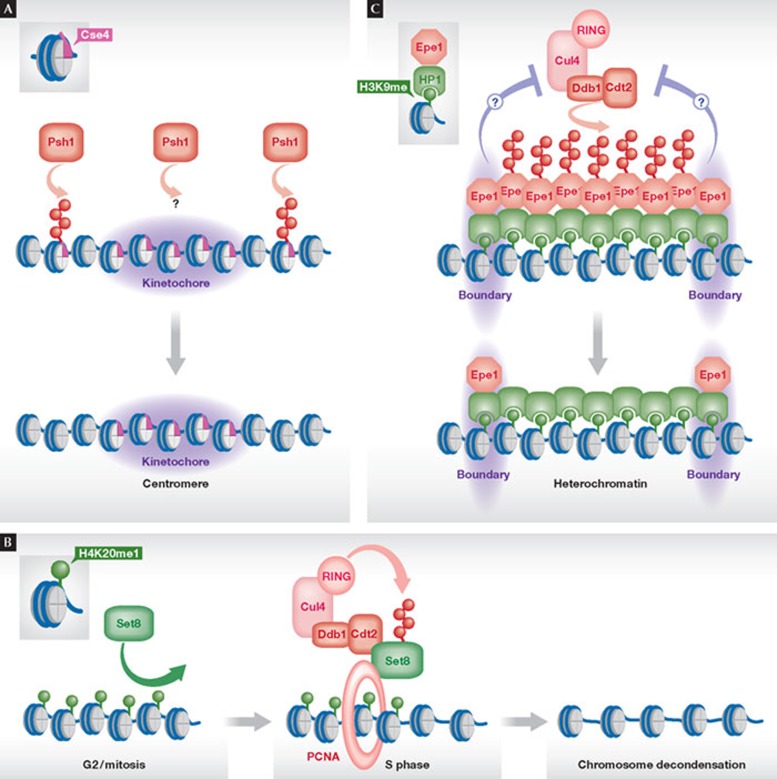
Figure 3. Shaping of chromatin by ubiquitin-dependent degradation.
(A) Shaping of centromeric chromatin by degradation of the histone H3 variant Cse4 by the E3 Psh1 at ectopic sites outside centromeres. (B) Shaping of S-phase-specific chromatin by degradation of the histone H4K20 mono-HMTase Set8/PR-Set7 by the E3 Cul4–Ddb1Cdt2. Polyubiquitylation requires the formation of a trimeric complex of Set8, Cul4–Ddb1Cdt2 and PCNA. (C) Shaping of heterochromatin boundaries through degradation of the anti-silencing factor Epe1 by Cul4–Ddb1Cdt2. Epe1 is recruited uniformly to heterochromatin by binding to HP1 proteins. Epe1 degradation within the body of heterochromatin results in its local accumulation at the boundaries. The signals preventing degradation of Epe1 at the boundaries are unknown. Cul4, Cullin 4; Cdt2, chromatin licensing and DNA replication factor 2; Ddb1, DNA damage-binding protein 1; Epe1, enhancer of position effect 1; HP1, heterochromatin protein 1; Set7/8, Sul(Var)3–9, Enhancer-of-zeste, Trithorax protein 7/8; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ.