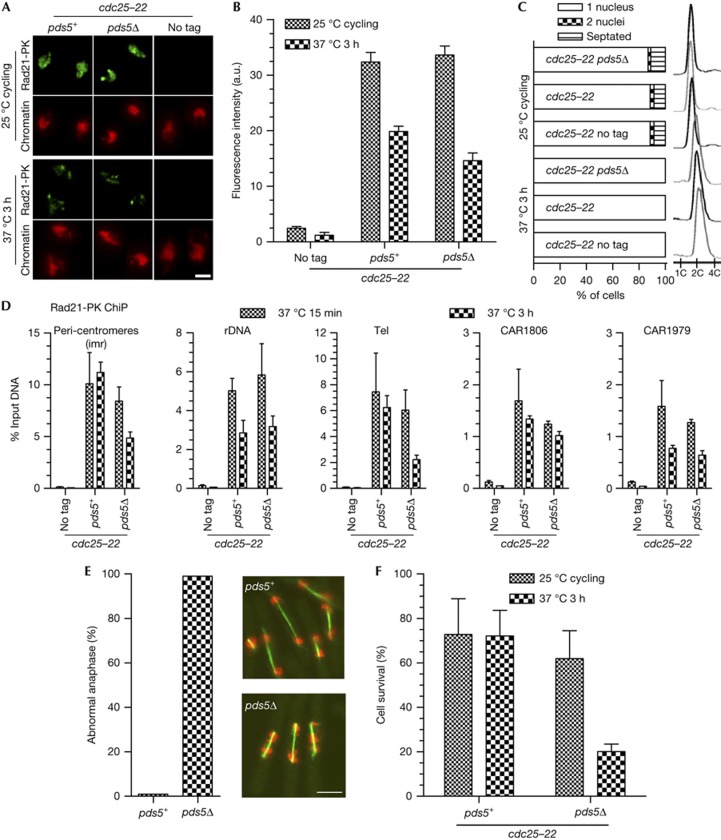
Figure 2.
Examination of Rad21 binding to chromosomes in pds5Δ cells upon prolonged G2 arrest. Cycling cells were shifted to 37 °C. The cdc25-22 mutation blocks entry into mitosis and keep cells in G2. (A) Images of Rad21-PK immunofluorescence on nuclear spreads from cells collected before and after 3 h at 37 °C. Chromatin was counterstained with DAPI. Bar=2 μm. (B) Quantification of Rad21 bound to chromosomes. Fluorescence intensity was measured for 50–100 nuclei per sample. Error bar=95% confidence interval of the mean with α=0.05. (C) Cell cycle staging showing that cells were predominantly in G2 before the temperature shift (one nucleus and 2C DNA content) and remained in G2 throughout the experiment. (D) ChiP assay showing the amount of Rad21-PK bound at the indicated loci, shortly (15 min) and 3 h after the 37 °C temperature shift. Error bar=s.d. from four ChiPs. (E) Cytological analysis of cells undergoing their first mitosis upon release from the cdc25-22 arrest. After 3 h at 37 °C, cells were shifted back to 25 °C and fixed 1 h later when most cells were in anaphase. The mitotic spindles were stained by indirect immunofluorescence against tubulin (green) and DNA was stained with DAPI (red, pseudocolour). Bar=5 μm. The frequency of abnormal anaphases was determined from the examination of 80–100 anaphases per sample. Abnormal anaphases were defined as cells with a spindle length>5 μm displaying DAPI-stained material that had not reached the spindle poles. (F) Cell survival was determined by plating cells back to 25 °C and scoring the number of colony-forming units. Error bar=s.d. from four (control) and five (pds5Δ) experiments. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.