Fig. 2.
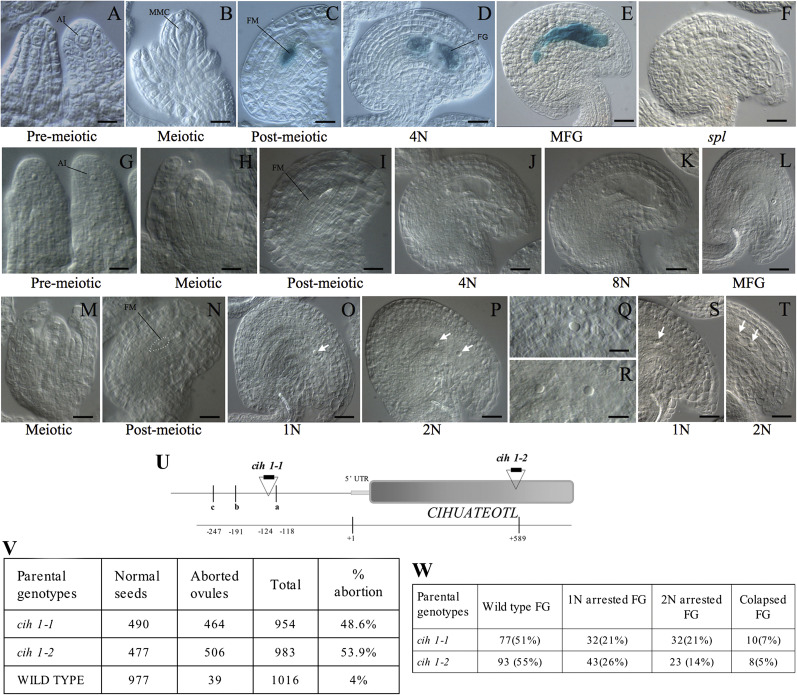
CIHUATEOTL is specifically expressed in the female gametophyte and its function is essential for female gametogenesis. Wild-type or cih-1 ovules were either histologically processed for GUS detection, or fixed and cleared for morphological analysis. (A-F) GUS expression in developing ovules of pCIH::GUS transformants. (G–L) Wild-type ovules showing normal female gametophyte development. (M–T) Mutant cih-1 ovules showing defects in female gametogenesis. (O) A mature cih-1 ovule shows a female gametophyte arrested at the one-nuclear stage (1N; arrow). (P) A mature cih-1 ovule shows a female gametophyte arrested at the two-nuclear stage (2N; arrows). (Q) Detail of a cih-1 ovule arrested at the one-nuclear stage. (R) Detail of a cih-2 ovule arrested at the two-nuclear stage. (S) A mature cih-2 ovule arrested at the one-nuclear stage of female gametogenesis (arrow). (T) A mature cih-2 ovule arrested at the 2-nuclear stage of female gametogenesis. (U) Genomic structure of the CIH locus; the position of allelic T-DNA insertions is indicated relative to the transcription initiation site. An I box promoter motif (a), a gibberelin-response motif (b), and a TATA box (c) are found in the regulatory region of CIH. (V) Developing siliques of cih-1 and cih-2 show close to 50% aborted ovules. (W) Frequency of phenotypic classes in cih-1 and cih-2 ovules. Scale bar: (A) 4 mm=7.2 μm; (B, Q, R) 4 mm=10 μm; (C, I, N) 4 mm=13.7 μm; (D) 4 mm=16 μm; (E, O) 4 mm=21 μm; (F) 4 mm=16.4 μm; (G) 4 mm=9.3 μm; (H) 4 mm=10.8 μm; (J) 4 mm=17.4 μm; (K, T) 4 mm=17.7 μm; (L) 4 mm=26.6 μm; (M) 4 mm=14.2 μm; (P, S) 4 mm=19.5 μm.