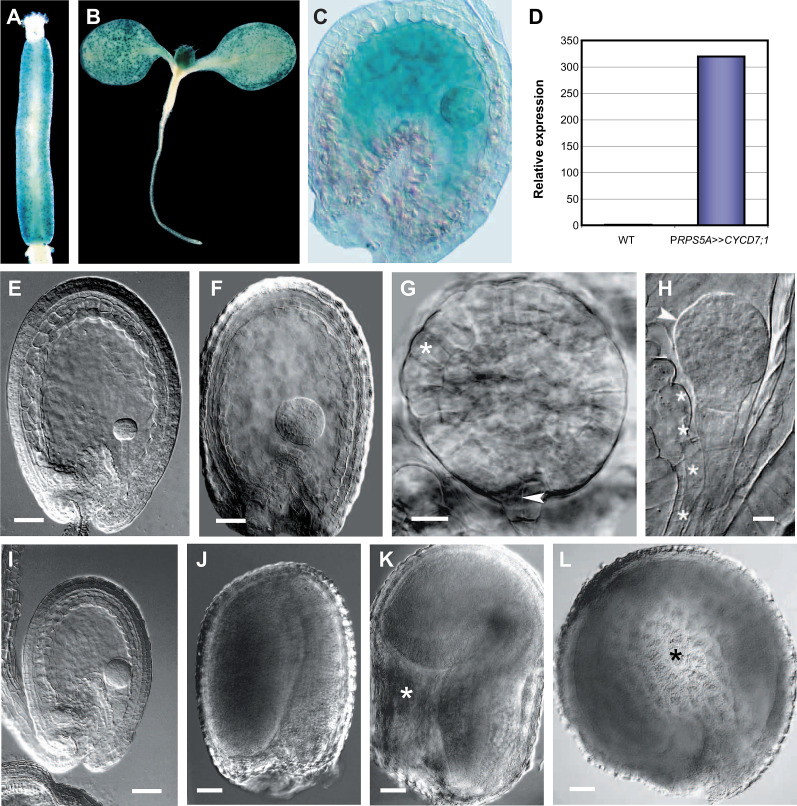
Fig. 8.
CYCD7;1 overexpression drives cell proliferation and cell growth in seed tissues. (A–D) Localization of GUS expression for pCYCD7;1:GUS (A, B) and cell-type-specific transactivation of CYCD7;1 in PRPS5A>>CYCD7;1 (C, D). (A) pCYCD7;1:GUS expression in stomatal cells lining the gynoecium. (B) pCYCD7;1:GUS expression in stomatal cells on the surface of developing leaves. (C) Global GUS activity in the embryo, suspensor, and endosperm of globular-stage seeds. (D) CYCD7;1 transcript levels in siliques containing globular-stage seeds: relative transcript abundance was scaled to expression in the wild type (1-fold expression). (E–L) Resulting phenotypic effects. (E) Wild-type globular seed. (F) PRPS5A>>CYCD7;1 seed containing an enlarged globular-stage embryo and endosperm. (G) Overproliferated PRPS5A>>CYCD7;1 globular-stage embryo showing enlarged protodermal cells (asterisk) and premature division of the hypophysis (arrowhead). (H) Overproliferated embryo with protuberances (arrowhead) and enlarged suspensor cells (asterisks). (I) Overproliferated embryo contained within a reduced endosperm. (J) Wild-type mature seed. (K) Enlarged PRPS5A>>CYCD7;1 seed with endosperm cavity (asterisk). (L) Enlarged PRPS5A>>CYCD7;1 seed with abnormal circular shape (cavity highlighted with asterisk). Bars = 50 μm (E, F, I–L), 20 μm (G, H).