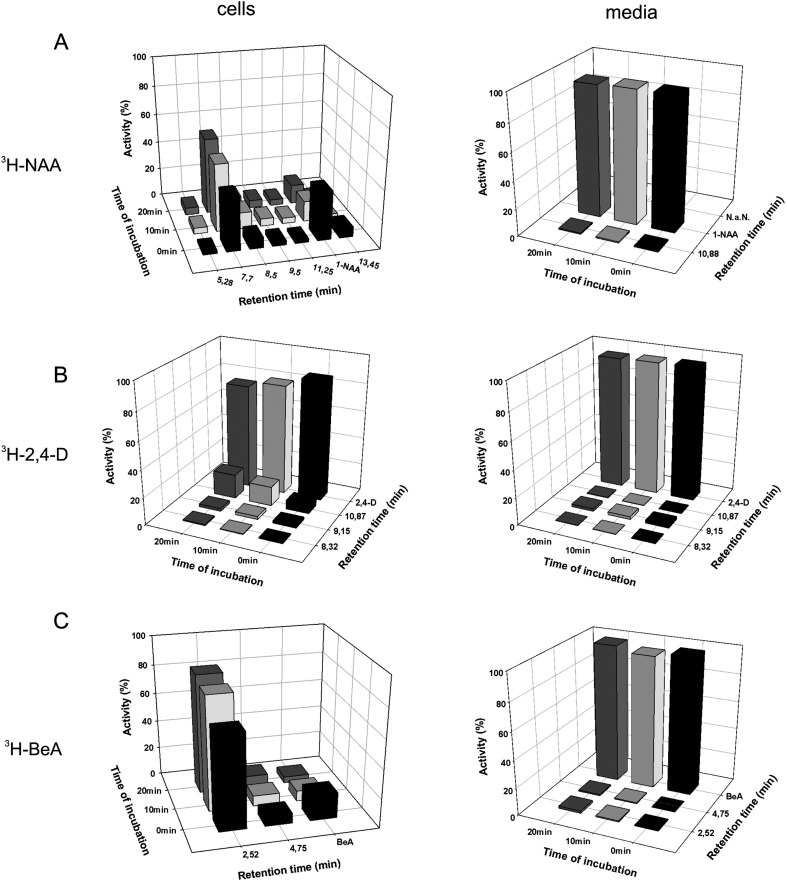
Fig. 1.
Metabolism of 3H-NAA, 3H-2,4-D, and 3H-BeA in tobacco BY-2 cells and in culture media. (A) NAA is rapidly metabolized to major metabolite M1 (identified as NAA glucosyl ester with a retention time of 7.7 min), which is predominant in the cells at 10 min and 20 min. No changes of NAA levels and only one minor metabolite peak were observed in the incubation medium, indicating that products of NAA metabolism (including the predominant NAA glucosyl ester) remained inside the cells. (B) 2,4-D is only partially metabolized to three unknown products. Thus the levels of 2,4-D slightly decreased during 20 min incubation, with a concurrent increase of an unknown metabolite at a retention time of 10.87 min. Levels of 2,4-D in the incubation medium remained constant and only three minor metabolites were observed, indicating that the products of 2,4-D metabolism also remained in the cells. (C) BeA was quickly metabolized to one predominant product at a retention time of 2.52 min (identified as BeA glucosyl ester) and one unknown minor product at a retention time of 4.75 min. A slight decrease of BeA content was observed in the incubation medium. Both metabolites were detected in the medium only as insignificant traces, indicating that these products remained in the cells. The percentages of individual peak activities were determined and normalized according to the corresponding activities in the total samples (100 %).