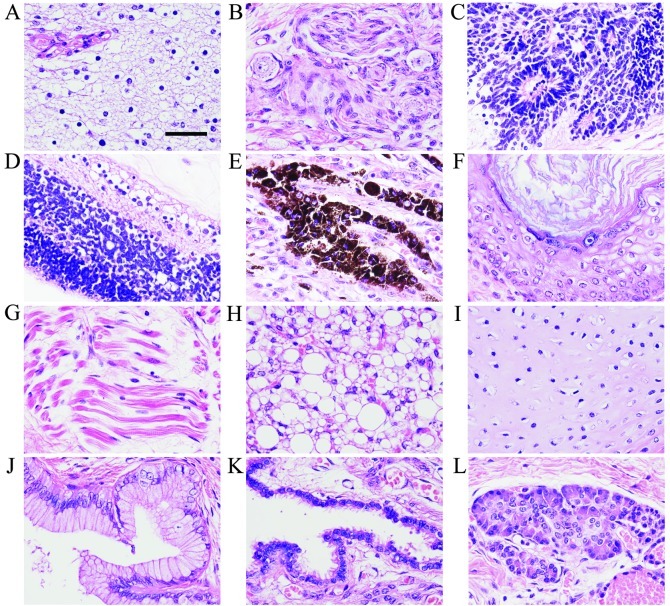
Figure 2.
Histopathological findings of the sacrococcygeal teratoma. The teratoma contained tissues from three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. The ectodermal tissues of the teratoma include brain tissue comprising (A) glia cells, (B) peripheral nerve with ganglion cells, (C) primitive neuroepithelium consisting of small hyperchromatic cells arranged in rosettes, (D) retina-like structure, (E) pigment epithelium containing melanin granules and (F) squamous epithelium with keratinization. The mesodermal tissues of the teratoma include (G) striated muscle fibers, (H) adipose tissue and (I) hyaline cartilage. The endodermal tissues include (J) columnar epithelium, (K) respiratory ciliated epithelium and (L) secretory gland-like structure. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Scale bar in (A), 30 μm.