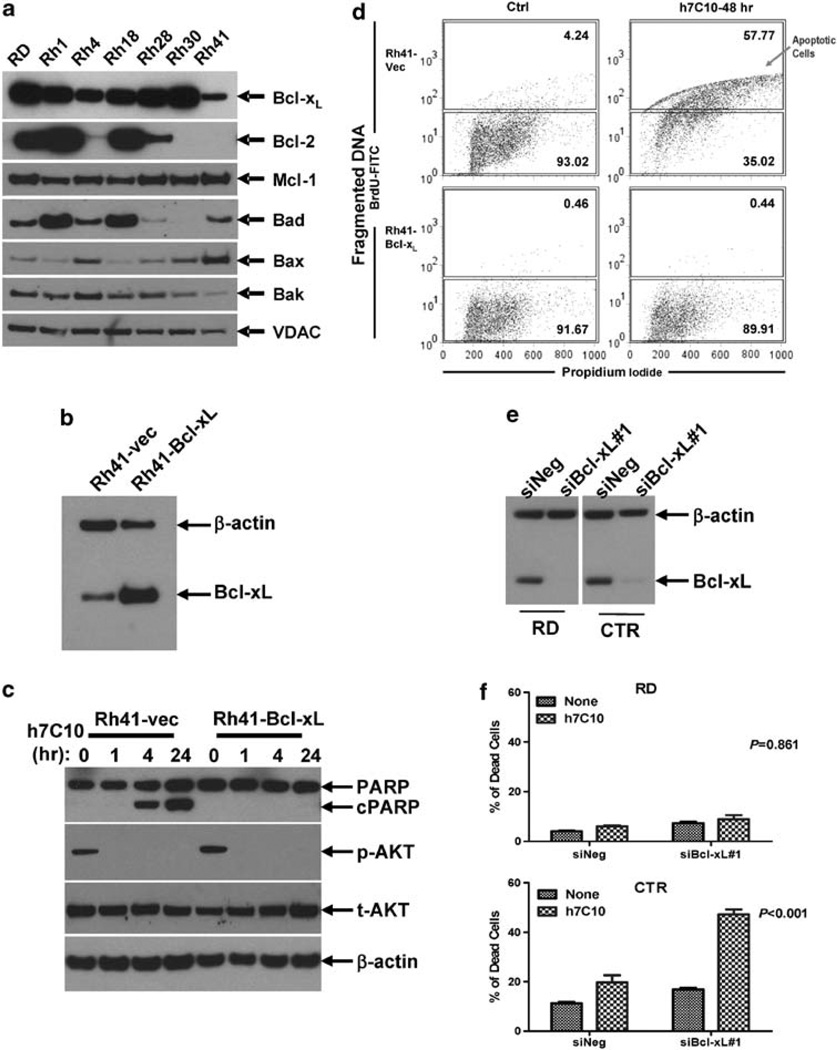
Figure 6.
Involvement of Bcl-xL in h7C10-induced cell death. (a) Analysis of the expression of pro-survival and pro-apoptotic proteins in RMS cell lines. (b) Generation of Bcl-xL lentivirus-infected Rh41 cells. Rh41 cells were infected with control and Bcl-xL lentiviruses and sorted with coexpressing GFP via FACS. The expression of Bcl-xL was verified by immunoblot. (c) Rh41-Bcl-xL and vector infected cells were treated with h7C10, lysates were used for the detection of p-AKT and cleaved PARP. (d) Rh41-vec and Rh41-Bcl-xL cells were treated with h7C10 for 2 days. The apoptotic cells were labeled with 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) and analyzed with FACS. Apoptotic cells have increased DNA fragmentation, and thus elevated BrdU-FITC signal. (e) RMS cells were transfected with siBcl-xL and the lysates were analyzed via immunoblot. (f) RMS cells transfected with siBcl-xL were further treated with h7C10. The percentage of dead cells was determined with cellometer. Statistic interaction P-values between h7C10 and siBcl-xL were determined using two-way ANOVA.