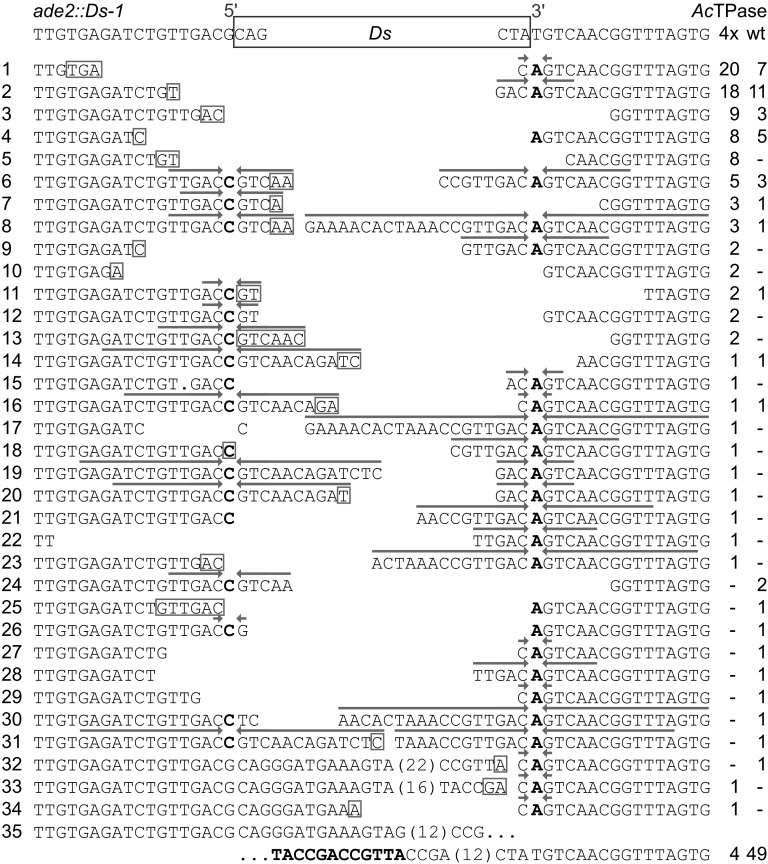
Figure 3 .
Ds excision footprints formed by AcTPase and AcTPase4x in yeast. The top row shows the sequence at the Ds insertion site in the yeast ADE2 gene. Rows 1–35 show the recovered Ds excision footprints and at the right their incidence in independent Ade+ revertants from wild-type AcTPase (wt) or hyperactive AcTPase4X (4x) expressing cells. Putative microhomologies at flanking DNA fusion sites are indicated as boxed nucleotides. Arrows above sequences highlight inverted repeats centered around the complementary bases C and A of the nucleotides bordering the Ds element that result from resolution of intermediate hairpin structures formed at the Ds-flanking host DNA during excision. Boldface letters in row 35 indicate the remaining copy of the 12-bp direct repeat in the Ds ends.