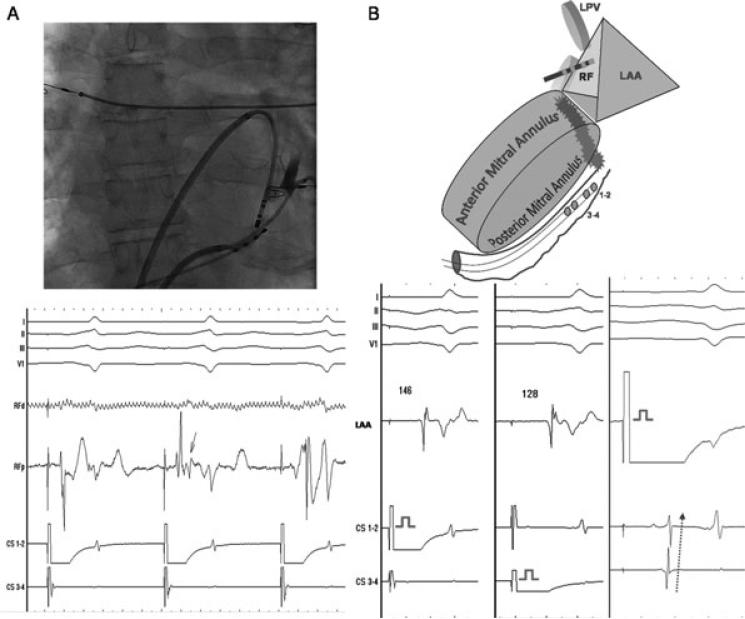
Figure 2.
A: Ablation with balloon occluded coronary sinus (shown in the fluoroscopic image) results in rapid-onset conduction delay (on RFp: from 72 milliseconds to 146 milliseconds) at the mitral isthmus after 4 minutes and 25 seconds of endocardial RF application. The arrow denotes the moment of split in the potential, which was followed by sudden prolongation of delay. B: Schema and electrograms demonstrating bidirectional block across the mitral isthmus during differential CS pacing, and pacing from the LAA at the end of the procedure. CS = coronary sinus; LAA = left atrial appendage; LPV = left pulmonary veins = RF = radiofrequency.