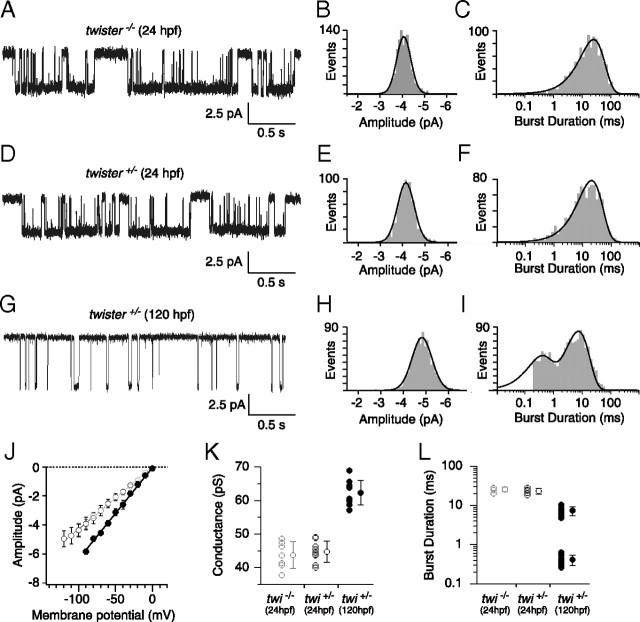
Figure 6.
Cell-attached ACh-activated single-channel currents from 24 and 120 hpf twister muscle. A, D, G, Sample traces of ACh-activated channels in 24 hpf twi−/− (A), 24 hpf twi+/− (D), and 120 hpf twi+/− fish (G). B, E, Amplitude distributions for 24 hpf twi−/− and 24 hpf twi+/− fish fit to single Gaussian distributions. C, F, Example semilog burst duration histograms fit to a single exponential function with time constants corresponding to 24.8 ms (n = 904 events) and 23.8 ms (n = 970 events) for 24 hpf twi−/− and 24 hpf twi+/− fish, respectively. H, Amplitude distribution for 120 hpf twi+/− fish fit with a single Gaussian function. I, Example burst duration histogram for 120 hpf twi+/− fish fit by the sum of two exponential components with time constants corresponding to 0.4 and 8.3 ms (n = 1170 events). J, Cumulative current–voltage relations comparing 24 hpf twi−/− (gray open circles; n = 7), 24 hpf twi+/− (black open circles; n = 9) and 120 hpf twi+/− (filled circles; n = 10) fish. A range of 17 to 140 events was used to calculate each point on the current–voltage relationship. K, Mean slope conductance ± SD calculated for 24 hpf twi−/− (43.7 ± 4.0 pS), 24 hpf twi+/− (44.7 ± 3.1 pS), and 120 hpf (62.3 ± 3.6 pS) shown alongside individual slope conductance values. L, The mean burst durations ± SD for 24 hpf twi−/− (25.6 ± 3.4 ms; n = 5), 24 hpf twi+/− (23.2 ± 3.9 ms; n = 5), and 120 hpf twi+/− (7.4 ± 1.9 ms and 0.41 ± 0.12 ms; n = 10) are shown along with the individual cell averages. A range of 376 to 1170 events was used to calculate the burst duration. All data were obtained using 30 nm ACh.