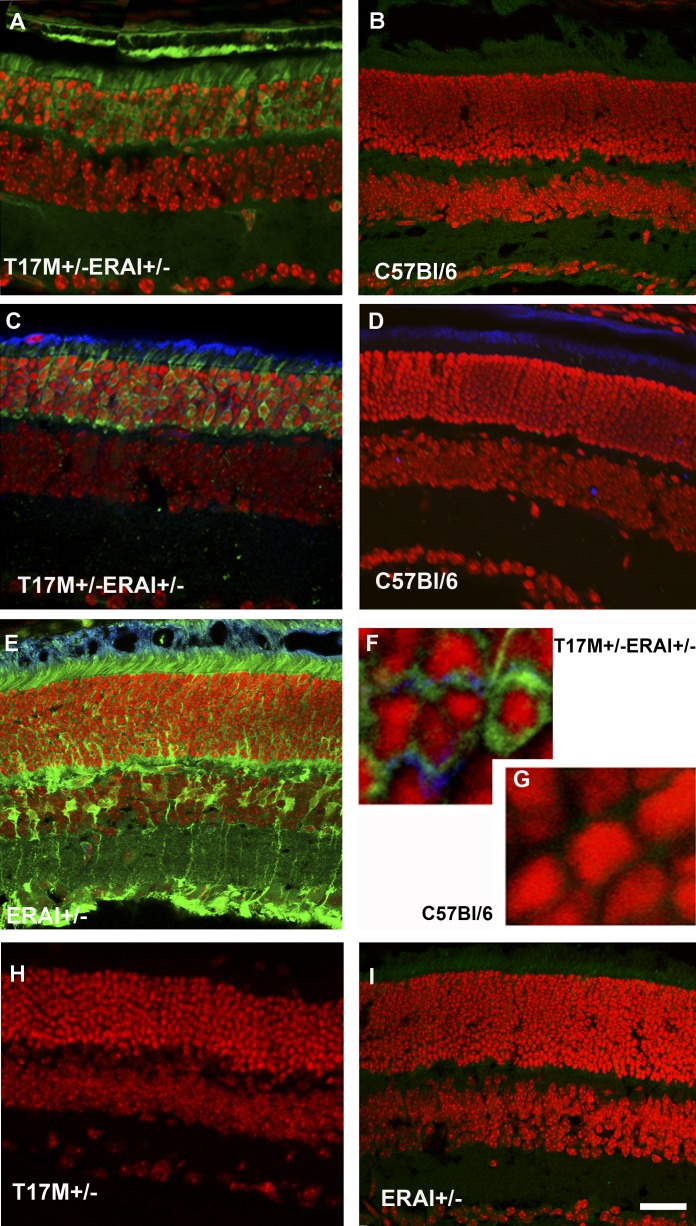
Figure 1. .
hT17M rhodopsin leads to activation of the ER stress response at P15 in T17M+/− ERAI+/− mice. Confocal microscopy is used to obtain images of mouse retinas. Propidium iodide is used to stain the nuclei (red). GFP protein expression (green) results from the splicing of the Xbp1-GFP transcription factor (detected by direct fluorescence or immunohistochemical analysis). For immunohistochemistry, an anti-GFP antibody is used to stain the sXbp1-GFP. The primary anti-rhodopsin antibody 1D4 and secondary anti-mouse Cy5-conjugated antibodies are applied to detect the localization of rhodopsin (blue). T17M+/− ERAI+/− (A) and C57BL/6 (B) images of retinas are obtained via direct observation under a fluorescence microscope. T17M+/− ERAI+/− (C), C57BL/6 (D), ERAI+/− positive control with tunicamycin injection (E), T17M+/− ERAI+/− (F), and C57BL/6 (G) images of retinas are obtained after immunostaining with anti-GFP and anti-rhodopsin antibodies. GFP fluorescence is observed in images T17M+/− ERAI+/− (A), T17M+/− ERAI+/− (C), ERAI+/− positive control with tunicamycin injection (E), and T17M+/− ERAI+/−(F), and not in the negative controls C57BL/6 (B), C57BL/6 (D), C57BL/6 (G), T17M+/− (H), and ERAI+/− (I). Accumulation of rhodopsin is observed in T17M+/− ERAI+/− (F) but is not detected in C57BL/6 (G). Scale bar indicates 30 μm (A–E, H, I) and 300 μm (F, G).