Figure 8.
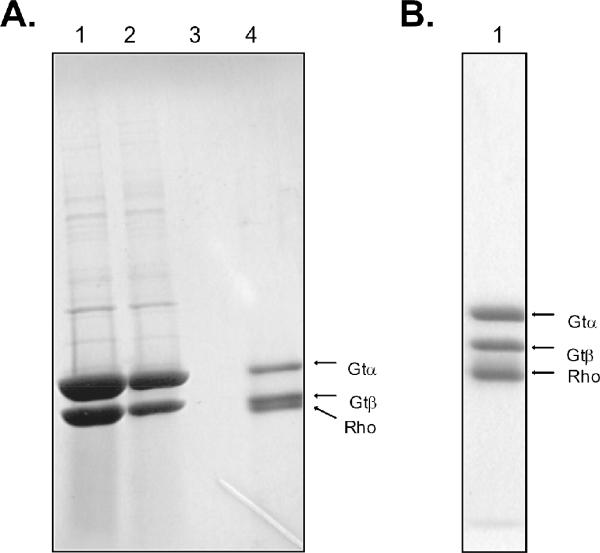
Purification of the complex using light activation of native and recombinant N2C,D282C rhodopsins. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of various fractions from 1D4-immunoaffinity purification of the rhodopsin/transducin complex using light-activated native rhodopsin isolated from bovine retina. Lane 1, transducin fraction applied to the immunoaffinity matrix; lane 2, unbound material; lane 3, last wash before elution of the complex; lane 4, fraction obtained upon elution with the 1D4-peptide. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of eluate from 1D4-column using light-activated recombinant N2C,D282C rhodopsin to form the complex. Only the α- and β-subunits of transducin are shown in the gels. Note that native rhodopsin migrates more closely to the β-subunit of transducin than does the N2C,D282C mutant as a result of the mutant having one less oligosaccharyl chain (at position 2 in the sequence). Samples were activated by exposure to room lights for 2 minutes following addition of transducin to rhodopsin immobilized on the solid support. Bands in the gels were visualized by staining with Coomassie blue.
