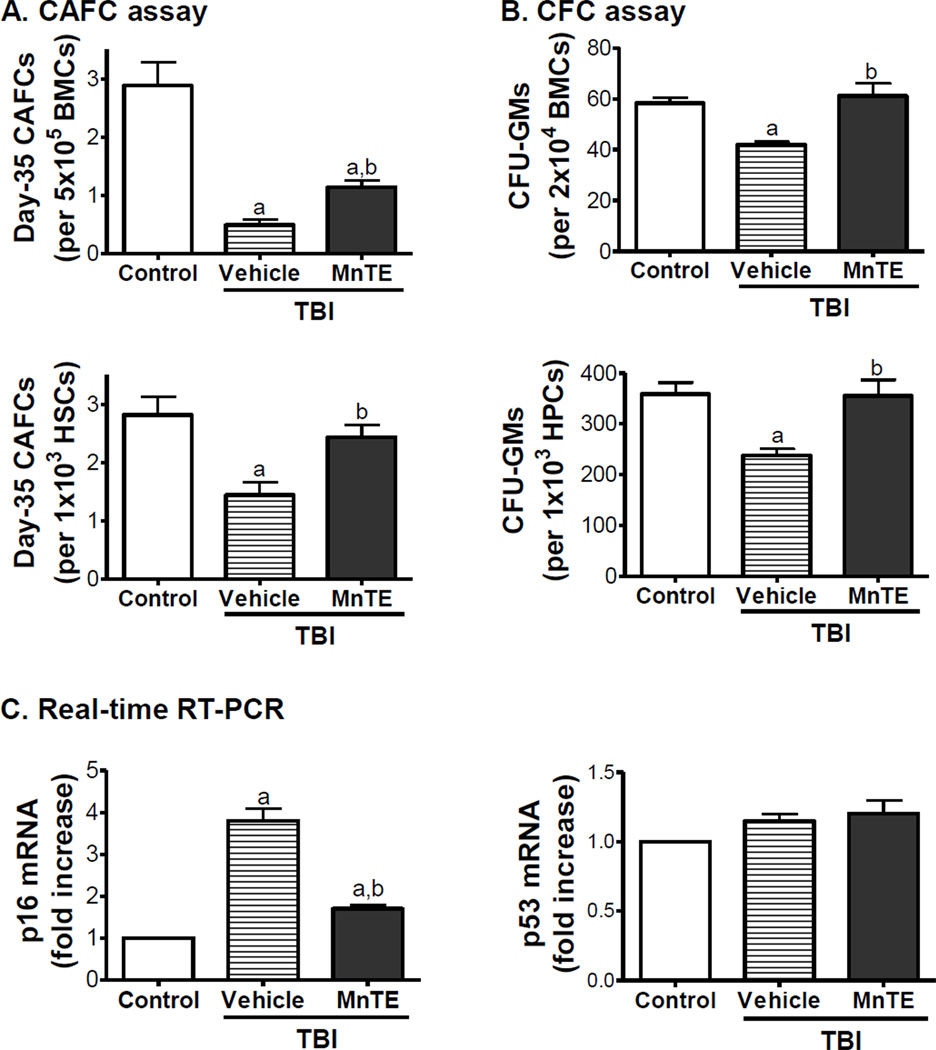
Fig. 4. MnTE mitigates TBI-induced residual BM injury in part by inhibition of HSC senescence.
Mice were un-irradiated as controls or irradiated and then treated with vehicle or MnTE as described above. A & B. The clonogenic function of HSCs and HPCs in BM-MNCs was measured by day-35 CAFC assay and CFC assay, respectively. The number of total day-35 CAFCs and CFU-GMs is also expressed as a function of HSCs and HPCs according to the frequencies of HSCs and HPCs in BM-MNCs quantified by flow cytometry. This is achieved by calculating the number of CAFCs and CFU-GMs in 1000 HSCs (Lin− c-kit+ Sca1+ cells) and HPCs (Lin− c-kit+ Sca1− cells), respectively, according to the formula: number of CAFCs or CFU-GMs / total number of HSCs or HPCs in 500,000 BM-MNCs × 1000. Data are presented as mean ± SE (N = 3). C. Analysis of p16 and p53 mRNA expression in HSCs by real-time RT-PCR. The data are presented as fold-change from controls (mean ± SE). a, p<0.05 vs. control; and b, p<0.05 vs. TBI with vehicle.