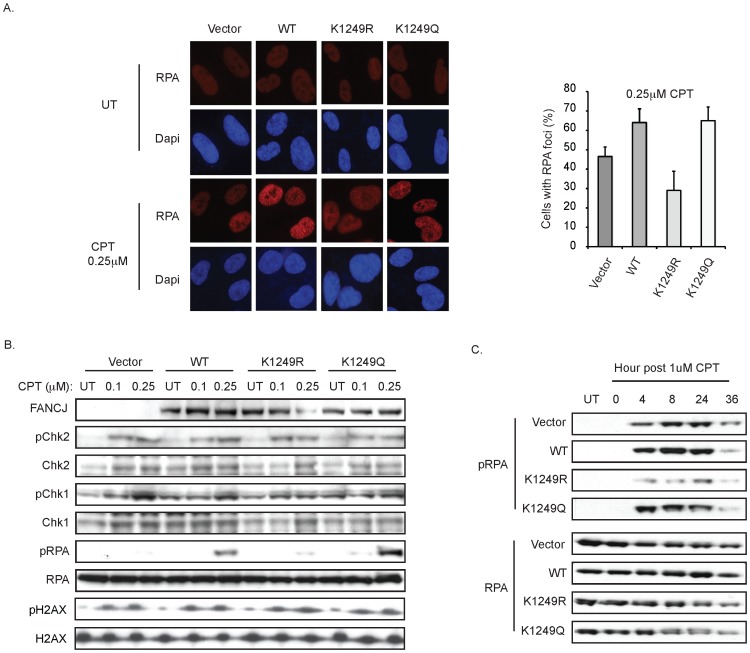
Figure 6. FANCJ and its acetylation at 1249 promote an RPA response.
A. Deficiency in FANCJ or its acetylation impairs the CPT-induced RPA focus formation. The FA-J cell lines were seeded onto 6-well plates, incubated overnight, left untreated or treated with CPT 1 h and immunoflourescence was performed with the indicated antibodies. The percent of cells with RPA foci was quantified and graphed. Data represent mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. B. FANCJ and its acetylation promote RPA phosphorylation at 1 h post-CPT. The complemented FA-J cell lines were either left untreated or treated for 1 h with the indicated dose of CPT and analyzed 1 h post-treatment. Cell lysates were collected, lysed, and analyzed with the indicated antibodies. C. FANCJ acetylation promotes RPA phosphorylation at times greater than 1 h post-CPT. Same as above but collected at the time points indicated.