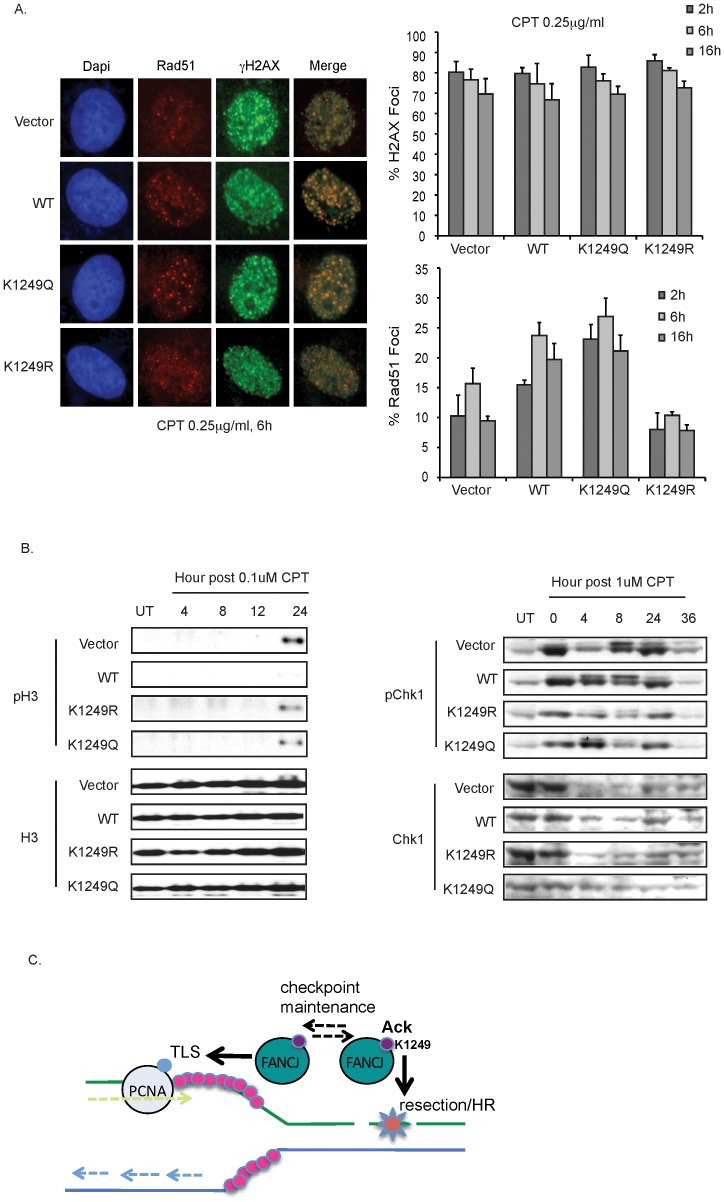
Figure 7. FANCJ and its dynamic regulation by acetylation promote resection-associated events.
A. Deficiency in FANCJ or its acetylation impairs the CPT-induced Rad51 focus formation. The FA-J cell lines were seeded onto 6-well plates, incubated overnight, left untreated or treated with CPT 6 h and immunoflourescence was performed with the indicated antibodies. The percent of cells with γ-H2AX and Rad51 foci was quantified and graphed. Data represent mean percent ± s.d. from three independent experiments. B. Deficiency in FANCJ or its ability to be regulated by acetylation impairs the CPT-induced checkpoint response. FA-J cell lines were either left untreated or treated for 1 h with the 0.1 µM or 1 µM of CPT and analyzed at the indicated time points. Cell lysates were collected, lysed, and analyzed with the indicated antibodies. C. Model depicts function of FANCJ acetylation in the DDR. FANCJ acetylation at lysine 1249 promotes resection and HR whereas de-acetylation promotes translesion synthesis (TLS). Maintenance of the checkpoint response; however requires the dynamic regulation of FANCJ acetylation.