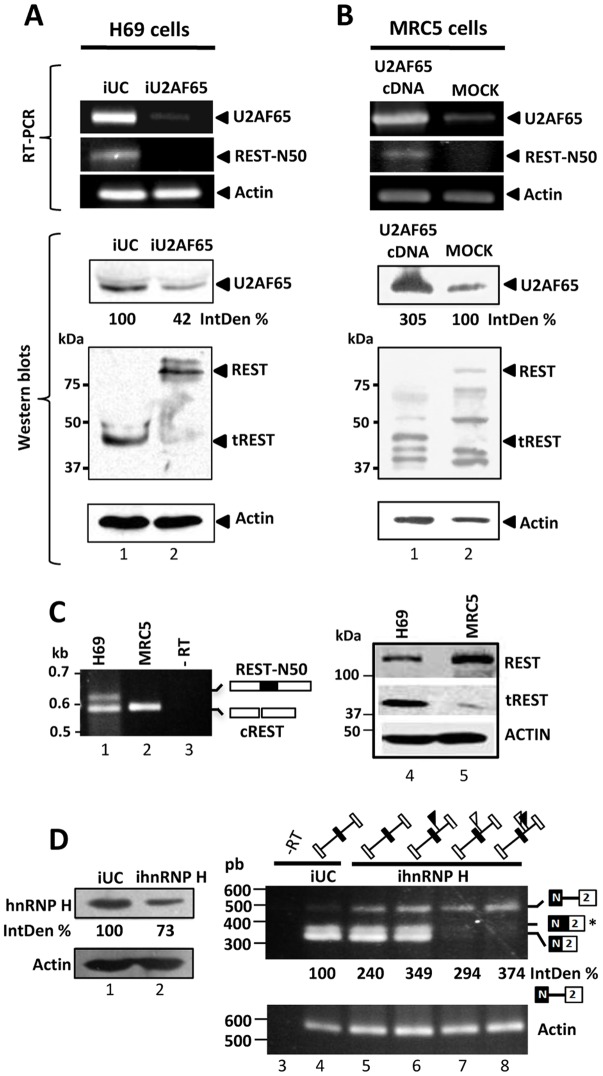
Figure 4. U2AF65 and hnRNP H are required for N50 exon activation in H69 cells.
(A) U2AF65 knockdown downregulates REST-N50 mRNA and tREST expression in H69 cells. H69 cells were treated with universal control (iUC) or U2AF65 siRNAs (lanes 1 and 2, respectively), (B) Overexpression of U2AF65 in MRC5 cells promoted REST-N50 mRNA and tREST expression. MRC5 cells were transfected with the U2AF65 cDNA (lanes 1) or with empty pcDNA3 vector (lanes 2). 24 h or 36 h post-transfection of siRNAs or cDNAs, respectively, the mRNAs coding for U2AF65, N50-REST, and Actin were monitored by RT-PCR. Protein expression of U2AF65, REST, tREST, and Actin was monitored by western blots as well. (C) Steady state expression profiles of REST mRNA variants (lanes 1–3) and protein isoforms (lanes 4–5) in H69 (lanes 1 and 4) and MRC5 (lanes 2 and 5) cells, respectively. No RT (- RT) PCR control reaction appears in lane 3. (D) hnRNP H knockdown leads to accumulation of unspliced N50/β-globin precursor. H69 cells were treated with iUC (lanes 1, 3 and 4) or hnRNP H siRNAs (lanes 2, 5–8). After 24 h, the cells were transfected with the wild type (lanes 3–5) or mutant N50/β-globin minigenes (lanes 6–8). 24 h post- transfection, N50/β-globin exon 2 splicing was monitored by RT-PCR (with primers SP6 and rtN62). No RT (- RT) PCR control reaction appears in lane 3. hnRNP H knockdown increased the unspliced precursors two-fold. Accumulation of the precursor increased up to 3 times when one or both of the N-PU (black flags) or G2-G3 (white flags) were mutated. Notably, G2-G3 mutants rendered no spliced products, and the N62/2 (*) product was obtained in double transfection experiments only. The PCR products and proteins were quantified densitometrically using the ImageJ software. IntDen % represents the expression change of the indicated protein or mRNA compared to their respective control treatment.