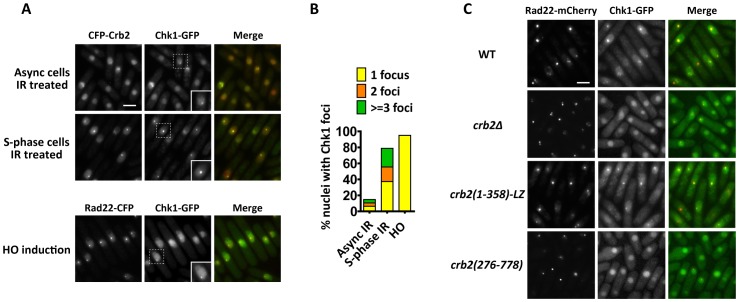
Figure 1. DNA damage-induced Chk1 focus formation requires the N-terminal 275 amino acids of Crb2.
(A) Chk1-GFP forms nuclear foci at IR- and HO-induced DSBs. For IR treatment, cells expressing Chk1-GFP and CFP-Crb2 were either treated with 80 Gy IR and incubated for 3 h, or first arrested in early-S phase by a 4-h treatment of 20 mM hydroxyurea (HU), and then treated with 80 Gy IR before releasing into HU-free medium and incubated for 3 h (S-phase IR treatment). For HO endonuclease induction, cells expressing Chk1-GFP and Rad22-CFP were shifted to thiamine-free medium for 16 h to induce the expression of HO, which is under the control of the thiamine-repressible nmt1 promoter. Strains used were DY6498 and DY6502. Bar, 5 µm. Inset, higher magnification of cells containing Chk1 foci. (B) Quantitation of Chk1 foci in (A). About 200 nuclei were scored for each condition. (C) The N-terminal region of Crb2 is required for Chk1-GFP foci. Cells expressing Chk1-GFP and Rad22-mCherry in wild type (WT), crb2Δ, crb2(1–358)-LZ or crb2(276–778) background were challenged with S-phase IR treatment as in (A). Strains used were DY6498, DY6497, DY6499 and DY6500. Bar, 5 µm.