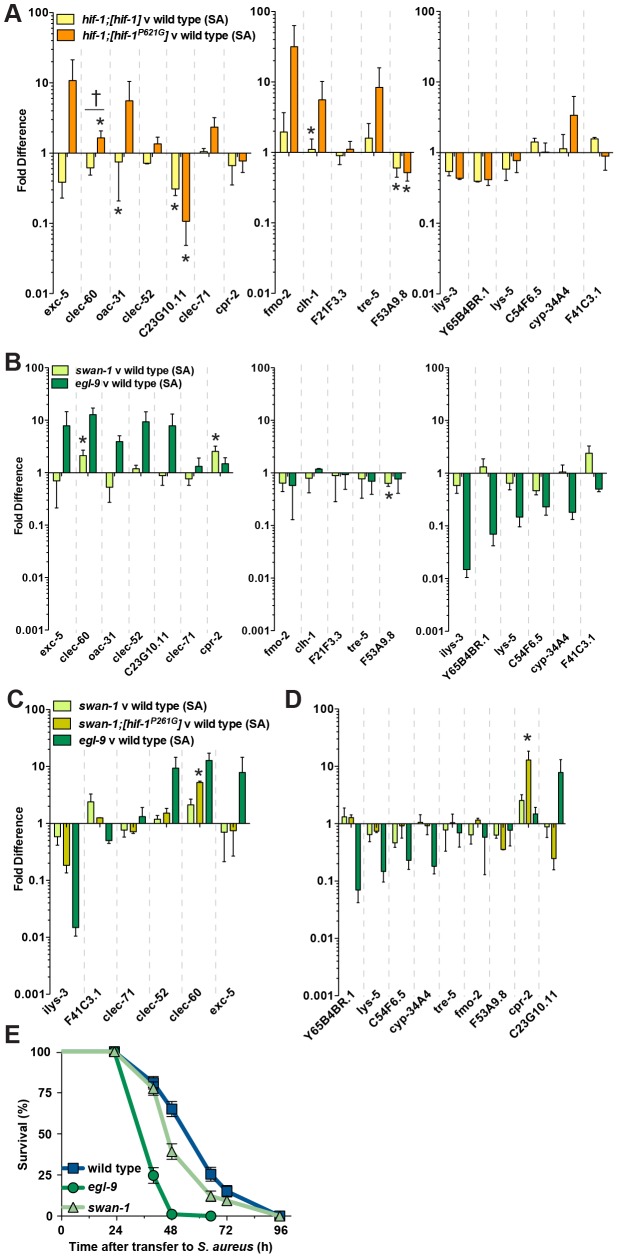
Figure 5. Noncanonical signaling contributes to lifting hif-1-mediated repression of the host defense response.
A. hif-1 animals overexpressing wild type HIF-1 (hif-1;[hif-1]) or non-hydroxylatable HIF-1 (hif-1;[hif-1P621G]) were infected with S. aureus for 8 h and gene expression, measured by qRT-PCR, was normalized to wild type. Data are means of 2 independent biological replicates, error bars are SEM. *, p≤0.05 (compared with wild type by two-sample t test); †, p≤0.05 (compared hif-1;[hif-1] with hif-1;[hif-1P621G] by two-sample t test). B. swan-1(ok267) mutants were infected with S. aureus for 8 h and gene expression, measured by qRT-PCR, was normalized to wild type. egl-9(sa307) data from Figure 3 are included for comparison. Results are means of 3–5 independent biological replicates, error bars are SEM. *, p≤0.05 (compared with wild type by two-sample t test). C. Genes whose expression levels were intermediate in swan-1; [hif-1P621G] animals compared with swan-1 and egl-9 animals. swan-1 animals overexpressing non-hydroxylatable HIF-1 (swan-1;hif-1P621G) were infected with S. aureus for 8 h and gene expression, measured by qRT-PCR, was normalized to wild type. Data are means of 2 independent biological replicates, error bars are SEM. *, p≤0.05 (compared with wild type by two-sample t test). Data for swan-1 and egl-9 mutants from Figure 5A and 3 are included for comparison. D. Genes whose expression levels did not appear intermediate in swan-1;hif-1P621G animals compared with egl-9 and swan-1 animals. Data for swan-1 and egl-9 mutants from Figure 5A and 3 are included for comparison. E. swan-1(ok267) mutants exhibit enhanced susceptibility to S. aureus. Survival analysis: wild type MS = 65 h, N = 110/4; swan-1 MS = 48 h, N = 108/1, p = 0.0036 (compared with wild type); egl-9 MS = 40 h, N = 87/2, p<0.0001 (compared with wild type). Results are representative of two independent trials, performed in triplicate.