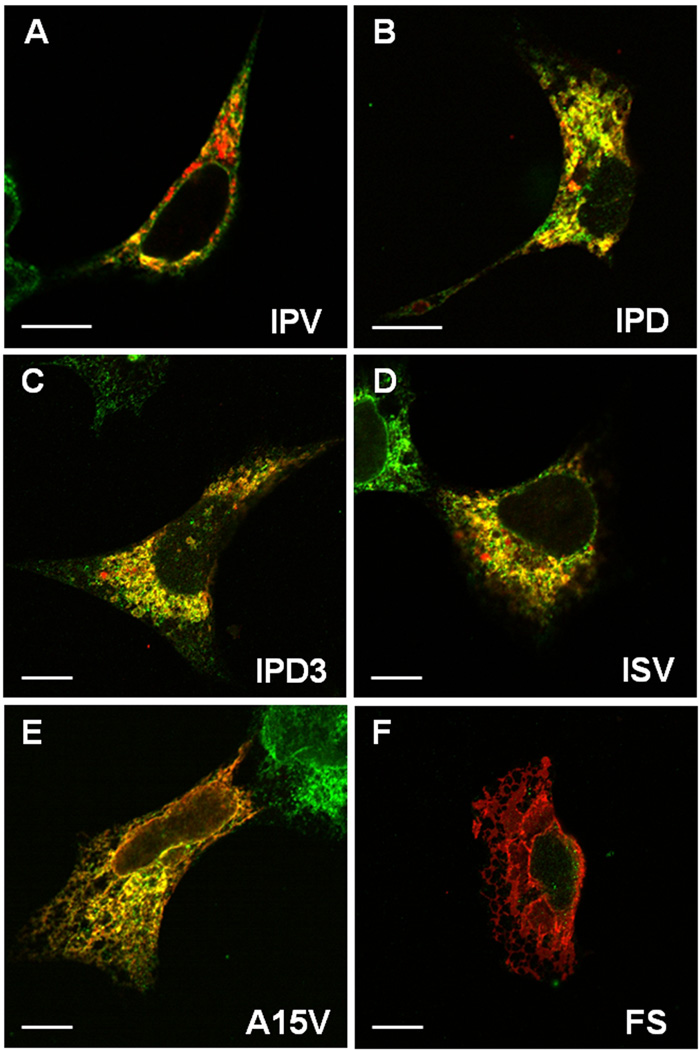
Fig. 5.
Confocal microscopy shows mutant DSPP proteins accumulate in the rER. Wildtype (IPV) DSPP (red) is observed predominantly in Golgi-like, punctate, perinuclear staining with limited co-localization (yellow) with rER marker (green, protein disulfide isomerase, PDI) (A). Representative DSPP mutants of the IPV motif (IPD, exon 3-skipping IPD3, and ISV, in red) all show predominant co-localization (yellow) with rER marker (green) (panels B–D). Note the monochrome rER (green) in adjacent, non transfected cells in some panels. A15V mutant (E) shows both rER co-localization (yellow) and some membrane-associated staining (red) suggesting that failure to remove leader sequence causes some protein to co-translationally insert into rER membranes and perhaps migrate into contiguous membranes such as nuclear membranes. Frameshift mutant protein (FS, Panel F) with its long hydrophobic amino acid domain shows predominant membrane-associated localization (red). HEK293 cells on glass coverslips were transfected with noted expression plasmids 24 hr prior to fixation, permeabilization, and cytostaining detected by confocal microscopy with rabbit anti mouse DSP (red) and mouse anti human PDI (green) via appropriate labeled second antibodies. Bars = 10 µm.