Fig. 4.
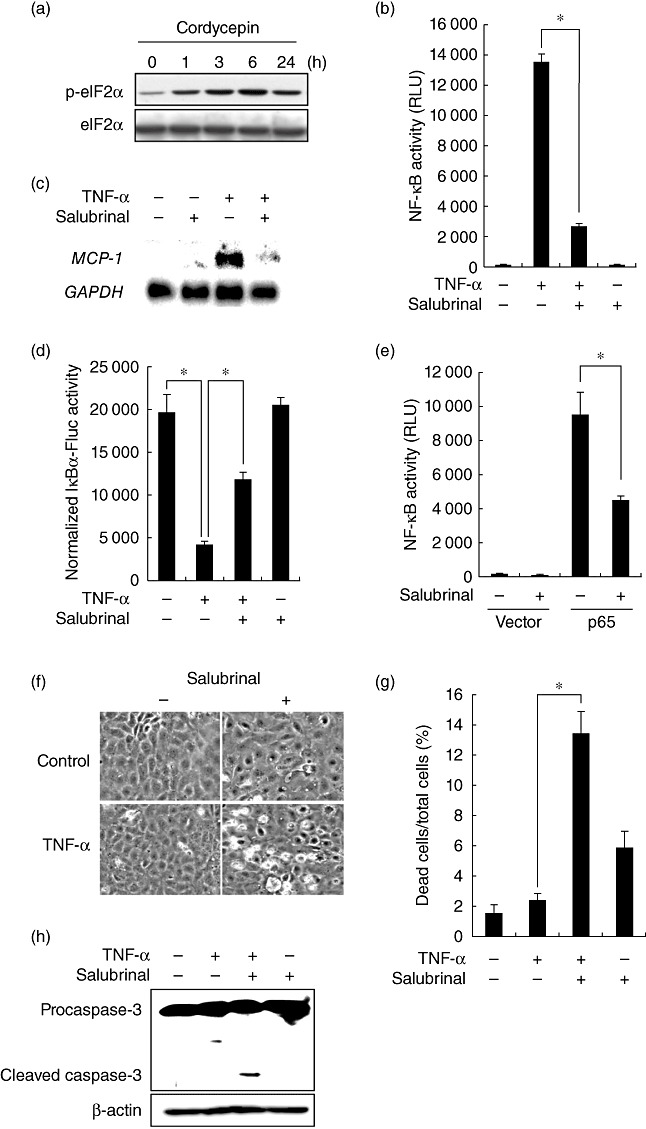
Inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)-κB by cordycepin through activation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α). (a) Cells were treated with cordycepin for the indicated time-periods and subjected to Western blot analysis of phosphorylated eIF2α (p-eIF2α). Total protein level of eIF2α is shown at the bottom as a loading control. (b) NRK/NF-κB-Luc cells were stimulated with tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the absence or presence of 50 µM salubrinal and subjected to luciferase assay. (c) Cells were treated with the indicated agents and subjected to Northern blot analysis. (d) Cells were transfected with pIκBα-Fluc or pCMV-Fluc, treated with TNF-α in the absence or presence of salubrinal and subjected to luciferase assay. The luciferase activity in pIκBα-Fluc-transfected cells was normalized by the levels of luciferase in pCMV-Fluc-transfected cells. (e) Cells were transfected with NF-κB-Luc together with empty vector or p65, treated with or without salubrinal and subjected to luciferase assay. (f,g) Cells were treated with TNF-α in the absence or presence salubrinal and subjected to phase-contrast microscopy (f) and assessment of cell death (g). (h) Cells were exposed to the indicated agents and subjected to Western blot analysis of caspase-3.
