Fig. 3.
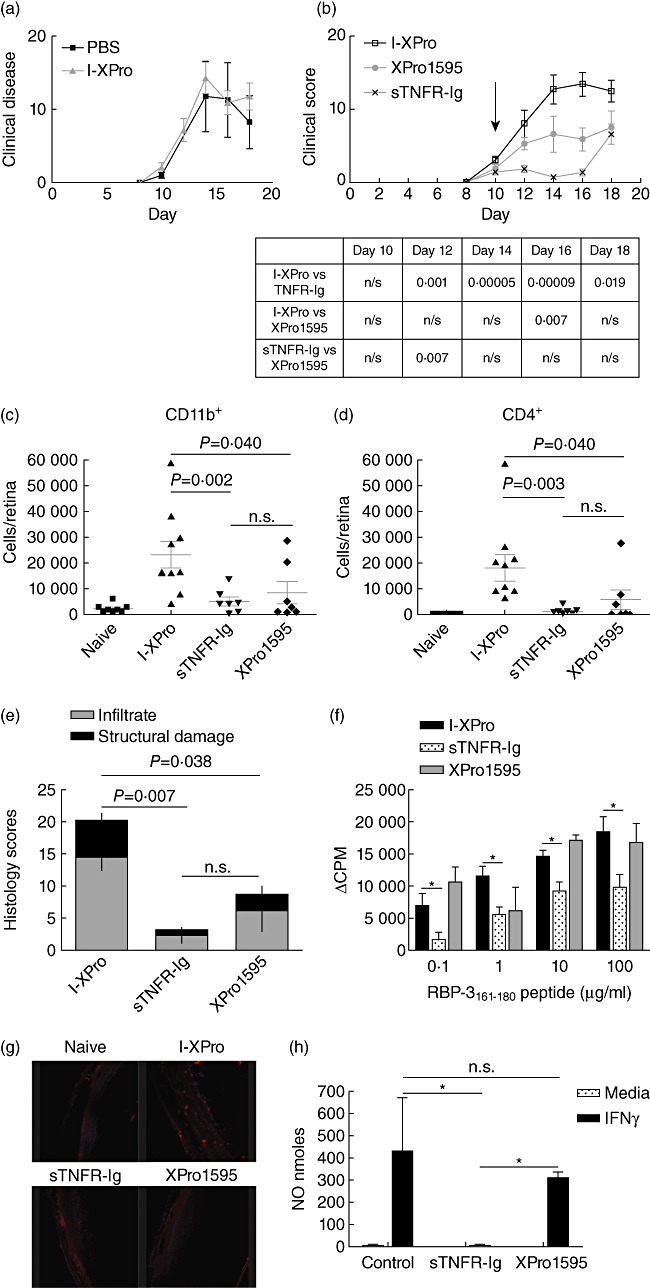
Inhibition of soluble tumour necrosis factor (sTNF) can suppress experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU). EAU was induced in B10.RIII mice, and on day 10 post-immunization (p.i.) the mice were treated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 10 mg/kg [in 100 µl phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)] I-XPro or 100 µ1 PBS. Clinical progression of disease with assessed by topical endoscopic fundus imaging (TEFI) from days 8 to 18; n = 4 mice per group (a). EAU was induced in B10.RIII mice, and on day 10 p.i. the mice were treated i.p. with 10 mg/kg of either I-XPro, sTNF receptor-immunoglobulin (sTNFR-Ig) or XPro1595 and the clinical progression of disease with assessed by TEFI from days 8 to 18. Treatment day is indicated by the arrow (b). The P-values for each day are tabulated below the graph. On day 18, the mice were killed and eyes taken for flow cytometric analysis of CD11b+ (c) and CD4+ (d) cells and histological analysis (e); mean ± standard error shown, n = 7–9 mice per group. On day 18 post-immunization, splenocytes were also used for a proliferation assay using 0·1–100 µg retinol-binding protein 3 (RBP-3)161–181 peptide (f); mean ± standard error shown. Eye sections from each mouse were also processed to detect nitrotryosine (red) and nuclear staining with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue), ×20 magnification (g). Naive mice were injected (i.p.) with 200 µg/mouse of I-XPro, sTNFR-Ig or XPro1595 and after 3 days the spleens removed and macrophages isolated using magnetic affinity cell sorting (MACS). The macrophages were stimulated in vitro with 100 U/ml interferon (IFN)-γ for 72 h prior to nitric oxide (NO) quantification; n = 3 (h).
