Fig. 4.
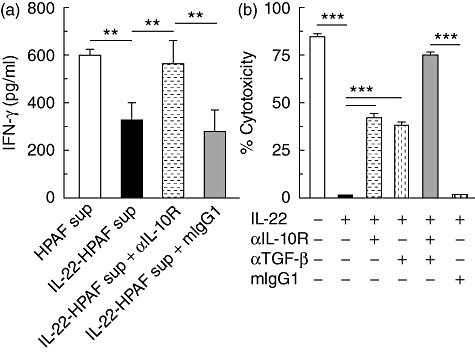
IL-22-mediated HPAFII suppression of Jurkat T cell IFN-γ production and NK-92MI cytotoxicity. (a) HPAFII cells were stimulated with IL-22 and supernatant collected after 24 h. Jurkat T cells were incubated with both PMA and supernatant derived from IL-22 activated HPAFII cells (black bar) for 24 h and IFN-γ secretion assessed by ELISA. Jurkat T cell IFN-γ production upon blockade of IL-10 signalling was determined by supplementation of cultures with αIL-10R (dashed horizontal bar). Jurkat T cells incubated with PMA and either supernatant from unstimulated HPAFII cells (white bar) or supernatant from IL-22-activated HPAFII cells and mouse immunoglobulin (Ig)G1 (grey bar) were included as controls. (b) NK-92MI cells were cultured for 4 h with IL-22-stimulated HPAFII target cells (black bar) at an effector : target ratio of 5 : 1 and cytotoxicity determined by LDH activity released by lysed cells. NK-92MI per cent cytotoxicity, upon cytokine blockade, was assessed by addition of αIL-10R (dashed horizontal bar), α-TGF-β (dashed vertical bar) or TGF-β (grey bar) antibodies. NK-92MI cells cultured with IL-22-stimulated HPAFII cells and mIgG1 (vertical hatched bar) or HPAFII cells preincubated in media alone (white bar) were included as controls. Columns represent the mean ± standard deviation. Comparable results for all conditions were obtained from three independent experiments for each. **P < 0·001; ***P < 0·0001.
