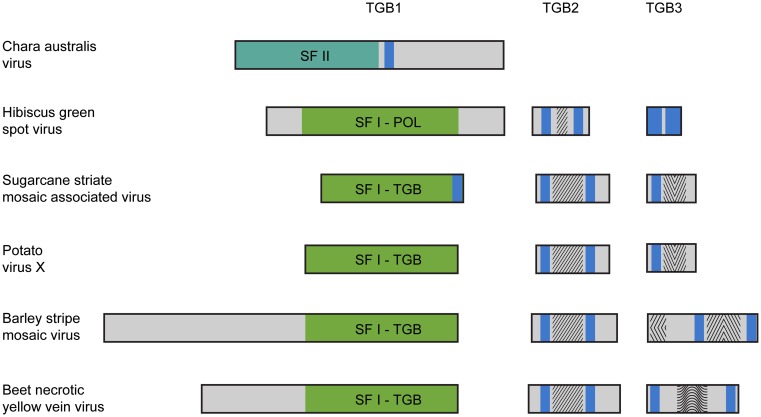
Figure 1.
Organization of triple gene block (TGB)-encoded proteins of some plant viruses. Boxes schematically represent open reading frames. It should be noted that in fact the TGB2 coding sequence overlaps the 3′ end of TGB1 gene, and the TGB3 ORF overlaps the 3′ end of TGB2 gene (Morozov and Solovyev, 2003). Helicase domains are indicated in the green boxes (SF-I) and dark green box (SF-II). Blue boxes represent the hydrophobic segments found in TGB proteins. Conserved sequence signatures in hydrophilic segments of TGB2 and TGB3 proteins are indicated by different shading within the boxes. In all studied TGBs, the TGB2 proteins have a highly conserved signature in the central part of their sequence. Note that the Hibiscus green spot virus TGB2 protein includes a shortened version of the TGB2 conserved signature. The TGB3 proteins are diverse in different virus groups. In Potato virus X and Sugarcane striate mosaic virus TGB3 proteins, a common signature is located downstream of their single transmembrane domain. This signature is characteristic for the TGB3 proteins in viruses of genera Potexvirus, Allexivirus, Mandarivirus, Carlavirus, and Foveavirus. In the Barley stripe mosaic virus, TGB3 has two unique signatures typical for viruses of the genera Hordeivirus and Pomovirus located in the N-terminal and central hydrophilic sequence segments. In the Beet necrotic yellow vein virus (BNYVV) TGB3, two transmembrane domains are located close to the protein termini, and there is a conserved signature characteristic of the genus Benyvirus only, which is located in the central protein part. The Hibiscus green spot virus TGB3 protein contains extremely short central hydrophilic region.