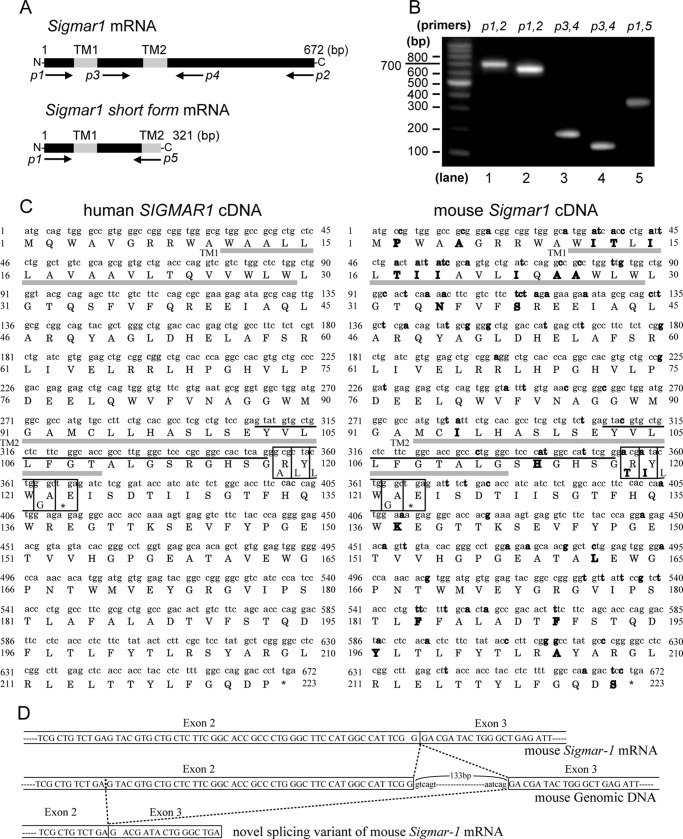
FIGURE 1.
σ1R alternative splicing. A, position of PCR primers relative to receptor sequences (transmembrane domain). B, PCR of an adult mouse brain hippocampus cDNA library was performed using the indicated oligonucleotide primers. C, sequence of coding region of human SIGMAR1 (left) and mouse Sigmar1 (right) cDNA. The deduced amino acid sequence is presented using the one-letter code. Differences between homologues are shown in bold. Two putative transmembrane domains (TM1 and TM2) are shown in gray underlines, and the 47-bp of sequences deleted from full-length σ1R are shown in black underlines. Their deletion results in a frameshift, giving rise to four novel amino acids in σ1SR (boxed). D, proposed splicing mechanism of σ1Rs. Exons are outlined, and coding sequence is denoted by capital letters. Intronic sequence is denoted by lowercase letters.