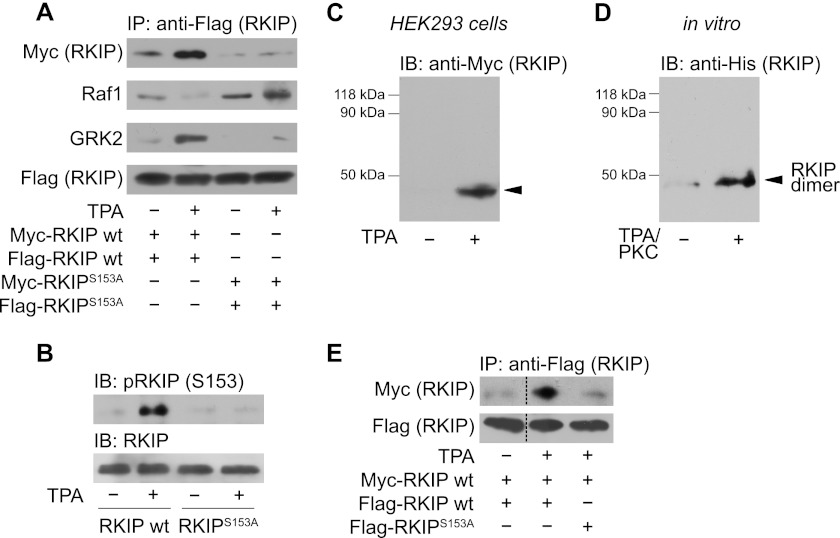
FIGURE 1.
PKC-mediated phosphorylation of RKIP at Ser-153 promotes RKIP-RKIP self-association. A, immunoprecipitation (IP) of wild-type FLAG-tagged RKIP (wt) and phospho-deficient FLAG-RKIPS153A from lysates of HEK293 cells and subsequent immunoblot analysis of co-immunoprecipitated Myc-RKIP wild-type (wt), Myc-RKIPS153A, Raf1, or GRK2. Cells were treated with TPA (1 μm, 5 min) as indicated. B, immunoblot analysis (IB) of Ser-153 (S153) phosphorylation of RKIP in the respective cell lysates of A. C, cross-linking experiments in HEK293 cells expressing wild-type Myc-RKIP. Cells were stimulated with TPA (1 μm, 5 min) as indicated and treated with paraformaldehyde (PFA; 0.75% (w/v), 7 min). Cell lysates were analyzed for RKIP complexes by immunoblotting. D, in vitro cross-linking experiments with purified His-RKIP using PFA (0.6% (w/v), 10 min). Cross-linking was performed before or after phosphorylation of His-RKIP by recombinant PKCδ (30 min, 30 °C). E, immunoprecipitation of FLAG-RKIP wild-type and FLAG-RKIPS153A from lysates of HEK293 cells treated without or with TPA (1 μm, 5 min) and subsequent Western blot analysis for co-immunoprecipitated wild-type Myc-RKIP. n = 4–7 independent experiments.