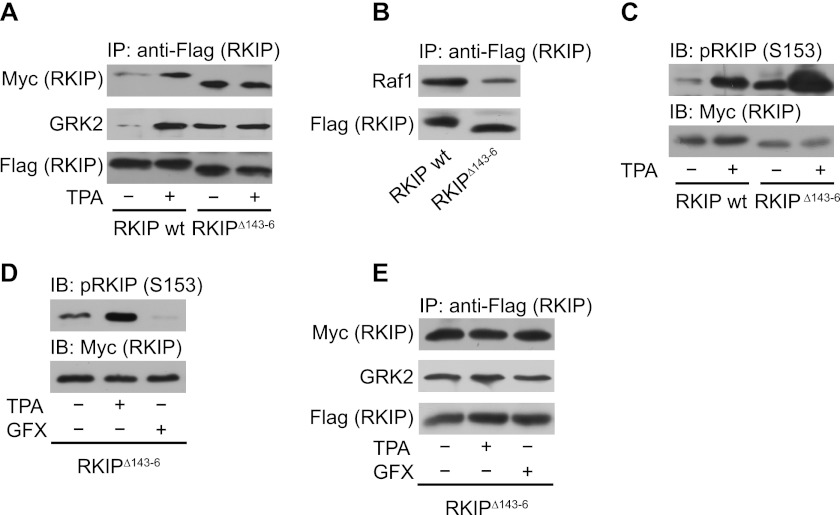
FIGURE 3.
RKIP lacking amino acids 143–146 has a high propensity for dimerization and GRK2 binding. A and B, immunoprecipitation (IP) of wild-type FLAG-RKIP (wt) or FLAG-RKIPΔ143–146 (RKIPΔ143–6) from lysates of HEK293 cells treated with TPA (1 μm, 5 min) as indicated. Co-precipitated wild-type Myc-RKIP (A), Myc-RKIPΔ143–146 (A), GRK2 (A), and Raf1 (B) were detected by Western blot analysis with the respective antibodies. The lower molecular mass of the deletion mutant RKIPΔ143–146 is visible due to the usage of 17% (w/v) acrylamide SDS-PAGE gels. C, immunoblot analysis (IB) of the respective cell lysates of A with anti-pRKIP (Ser-153, S153) antibodies. D, immunoblot analysis of Ser-153 phosphorylation of overexpressed RKIPΔ143–146 in HEK293 cells pretreated with either TPA (1 μm, 5 min) or bisindolylmaleimide I (GFX; 3 μm, 2 h) as indicated. E, immunoprecipitation of FLAG-RKIPΔ143–146 from cells pretreated with either TPA (1 μm, 5 min) or GFX (3 μm, 2 h) as indicated with subsequent immunoblot analysis of co-immunoprecipitated Myc-RKIPΔ143–146 or GRK2. n = 4–7 independent experiments.