FIGURE 4.
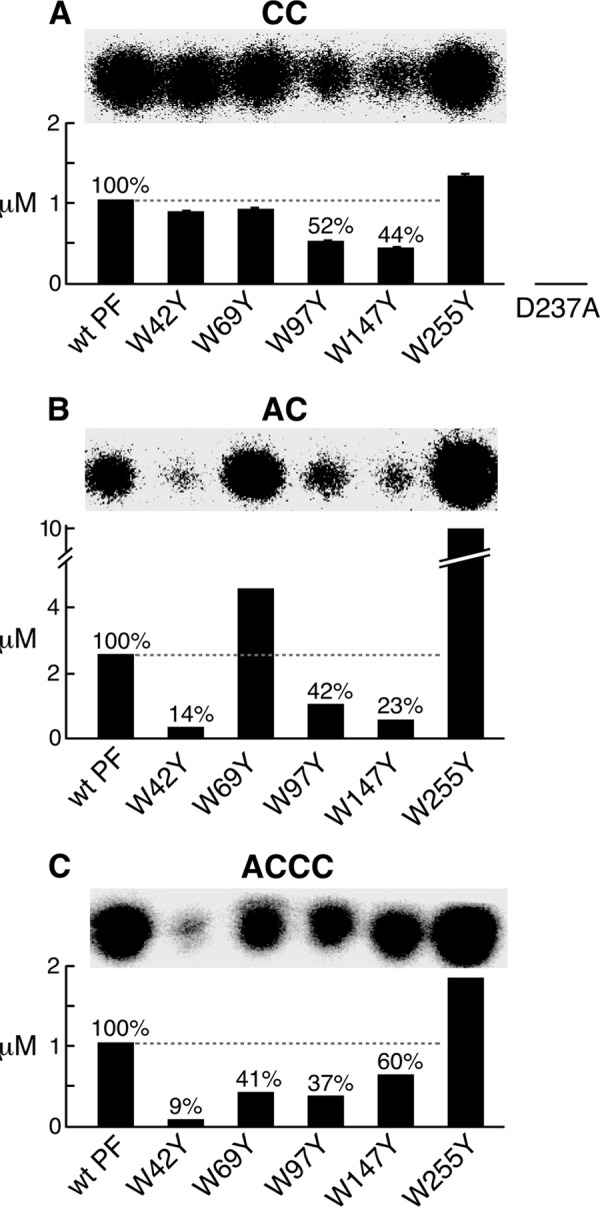
Catalytic activity, diribonucleotide synthesis, and diribonucleotide extension. A, template-independent diribonucleotide synthesis. The standard reaction contained a 2 μm concentration of the indicated primase and 1 mm [α-32P]CTP (0.1 mCi/ml) in buffer C. Wild-type primase fragment, primase fragments containing one tryptophan replaced with tyrosine, and primase-D237A were used in these experiments. After incubation at 23 °C for 1 h, the product pppCC was dephosphorylated with CIAP to yield CC. The product CC was separated, and its amount was determined. The percentage was calculated by assigning a value of 100% for the wild-type primase fragment. The S.E. values (error bars) were obtained from two independent experiments. B, template-directed diribonucleotide synthesis. Reactions contained a 0.4 μm concentration of the indicated primase, 4 μm template 3 containing 5′-AAGTC-3′ (Table 1), 1 mm ATP, and 1 mm [α-32P]CTP (0.1 mCi/ml) in buffer B. After incubation at 23 °C for 30 min, the product pppAC was dephosphorylated to AC as described in A. The amount of AC synthesized by each primase was determined as in A. C, template-dependent extension of diribonucleotide. The reaction contained 0.4 μm indicated primase, 4 μm template 4 containing 5′-GGGTC-3′ (Table 1), 1 mm 5′-AC-3′, and 1 mm [α-32P]CTP (0.1 mCi/ml) in the same buffer B. After incubation at 23 °C for 30 min, the products were separated, and the amount of ACCC was measured as in A.
