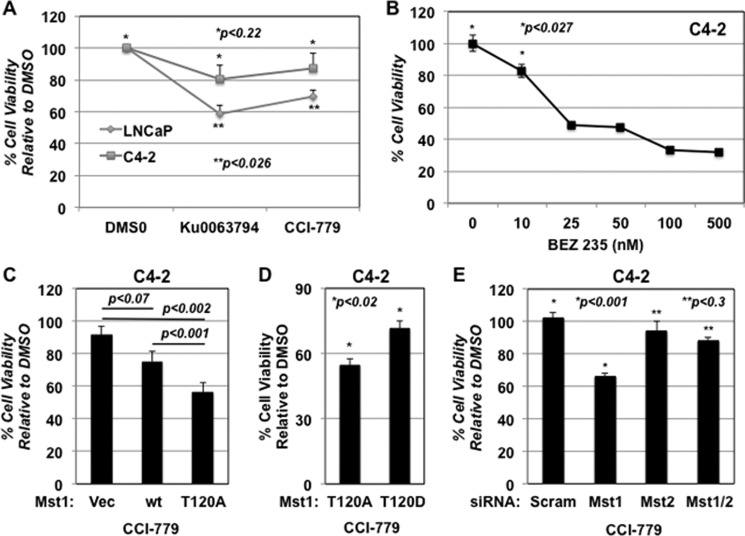
FIGURE 4.
Phopsho-Mst1-Thr-120 appears to be associated with C4-2 prostate tumor cell resistance to mTOR inhibitors. A, LNCaP or C4-2 cells were treated with DMSO, Ku0063794 (1 μm), or rapamycin (1 μm). B, C4-2 cells were treated with increasing doses (0, 10, 25, 50, 100, and 500 nm) of the dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor BEZ 235. Control or drug treatments were performed in T medium supplemented with 5% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. C, effects of CCI-779 (0.5 μm) on C4-2 cells engineered to express vector, Mst1-WT, or Mst1-Thr-120A mutant. D, effects of CCI-779 (0.5 μm) on C4-2 cells that were transiently transfected with phosphorylation-deficient Mst1-Thr-120A or phosphomimetic Mst1-T120D in a 96-well plate in triplicates, followed by CCI-779 treatment. 100 ng of plasmid DNA was used per well. An MTS assay (A 490 nm) at 48 h post-drug treatment was performed to determine cell viability in experiments A, B, C, and D. E, effects of DMSO or CCI-779 (0.5 μm) on C4-2 cell viability with scramble control, Mst1, Mst2, and Mst1/2 knockdown conditions. Gene-specific siRNA was used to knock down Mst1, Mst2, or Mst1/2 protein in a transient transfection assay. Cell viability was determined by MTS (A 490 nm) at 72 h post-transfection. Data are representative of multiple experiments.