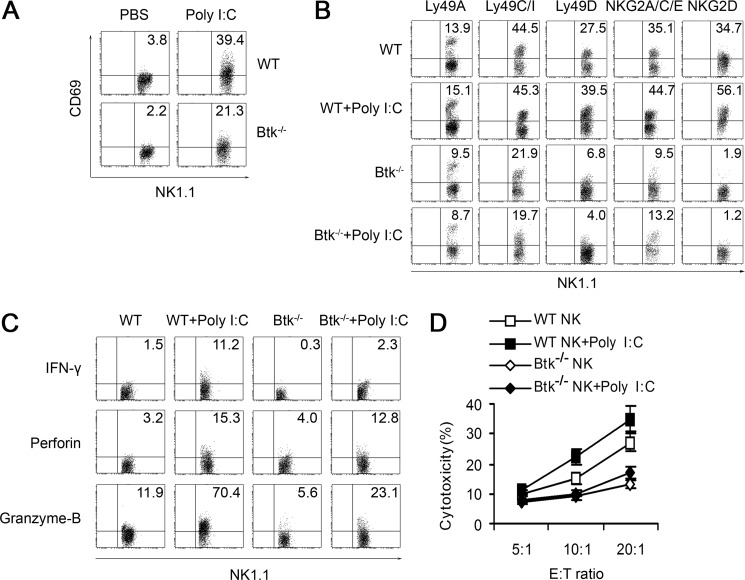
FIGURE 2.
Btk deficiency leads to the impaired activation of murine NK cells in response to TLR3 ligand. A, CD69 expression of splenic WT or Btk−/− NK cells with or without stimulation of poly(I:C). B, Ly49A, Ly49C/I, Ly49D, NKG2A/C/E, and NKG2D expression on splenic WT and Btk−/− NK cells with or without stimulation of poly(I:C). C, intracellular IFN-γ, perforin, and granzyme-B expression of WT and Btk−/− NK cells. D, cytotoxicity of WT and Btk−/− NK cells against YAC-1 cells. Data are mean ± S.D. of triplicate experiments. All experiments above were performed four times with similar results. Data are means ± S.E. of triplicate experiments.