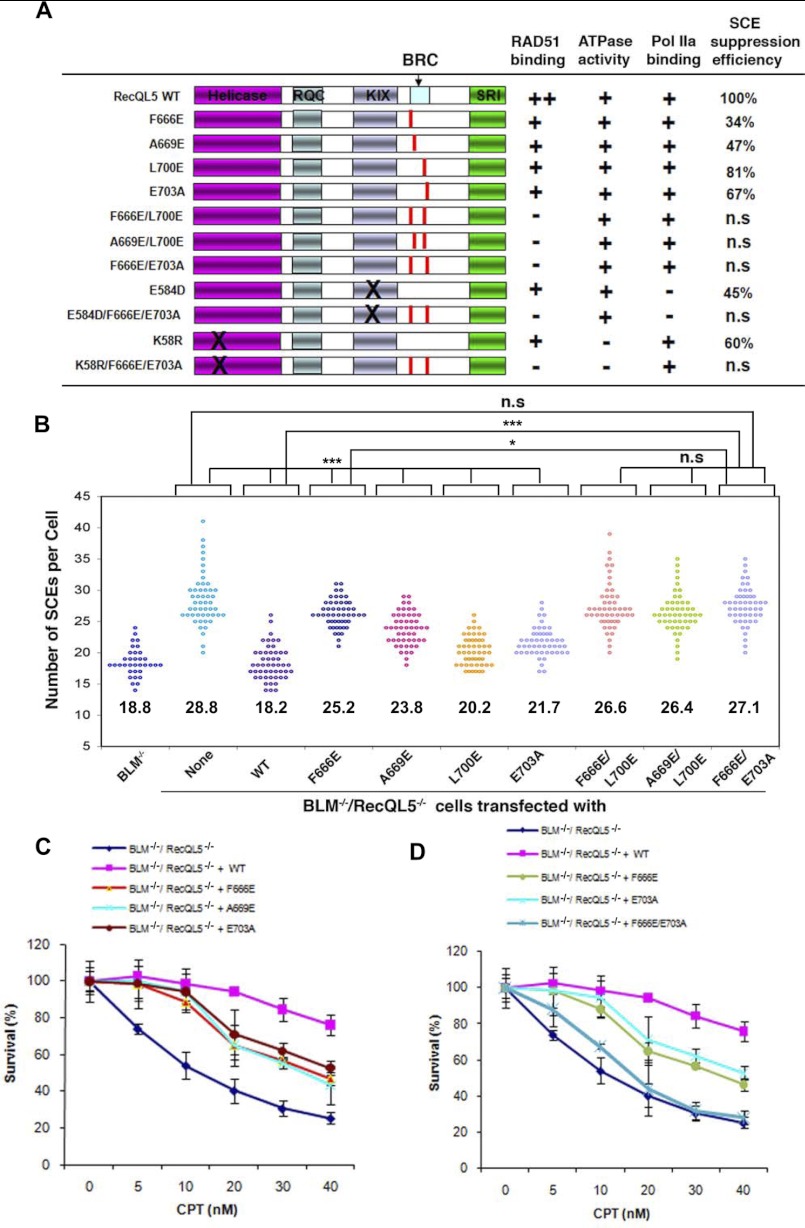
FIGURE 4.
RECQL5 mutants deficient in RAD51 interaction are defective in suppression of SCE and resistance to CPT. A, summary of different human RECQL5 mutants and their corresponding activities in association with RAD51, ATPase activity, Pol IIa binding, and suppression of SCE. Different RAD51 association is indicated as follows. ++, normal; +, reduced; −, nearly completely lost. SCE values are shown as a percentage. The suppression efficiency for the wild type protein was set to 100%. Lower suppression efficiency correlates with stronger defect. n.s, statistically not significantly different from the BLM−/−/RecQL5−/− cells. B, scatter plot showing the SCE levels of BLM−/−/RecQL5−/− DT40 cells complemented by the wild type and various mutants of RECQL5 as shown in A. Each point represents the total number of SCEs in a single mitotic spread. Conditions that show significant differences of p value <0.05 or p value <0.0001 are shown as one or three asterisks, respectively. The mean number of SCEs/cell is shown for each mutant, which was determined by examining chromosome spreads of three independent groups of metaphase cells (50 cells per group). C and D, CPT sensitivity curves of BLM−/−/RecQL5−/− DT40 cells complemented with WT and different RECQL5 mutants, as indicated. Two different clones were tested for each mutant in order to ensure that the results are not due to clonal variation. Mean and S.D. (error bars) from three independent experiments are shown.