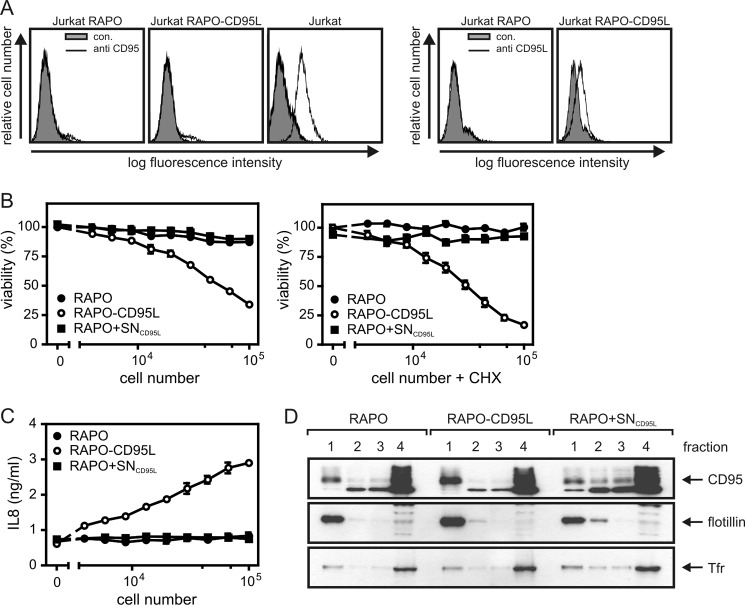
FIGURE 2.
Cells expressing membrane-bound CD95L induce efficient CD95 translocation into lipid rafts. A, FACS analysis of CD95 and CD95L expression of the CD95-deficient Jurkat RAPO clone and a membrane-CD95L-expressing transfectant derived thereof. B and C, HT1080 cells (2 × 104 cells/well) were seeded in 96-well plates. The next day, medium was replaced by medium containing the indicated amounts of RAPO or RAPO-CD95L cells. As an additional control RAPO cells suspended in supernatant of RAPO-CD95L cells (RAPO+SNCD95L) was used. Cell death induction (B) was analyzed in the presence and absence of CHX measuring cell viability after 18 h using crystal violet staining. To determine IL8 production, supernatants were analyzed by ELISA (C). D, HT1080 cells were cocultivated for 4 h with RAPO, RAPO-CD95L cells, and again RAPO cells supplemented with supernatant of RAPO-CD95L cells containing soluble CD95L (RAPO+SNCD95L). Triton X-100 lysates of the various cocultures were then fractionated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation, and fractions were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of CD95. The upper fraction (1) again contained the insoluble membrane fraction with lipid rafts, and soluble proteins were again present in fraction 4.