Figure 3.
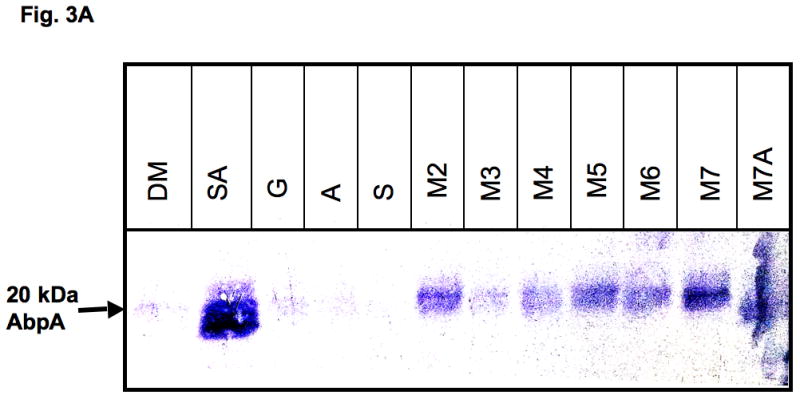
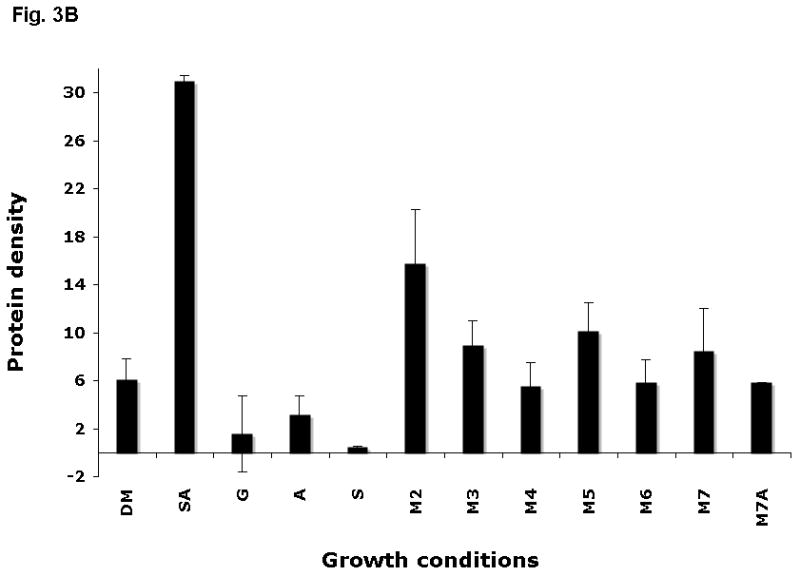
Expression of AbpA protein in culture supernatants grown with different malto-oligosaccharides. (A) Bacterial cells derived from the same culture were incubated for 40 min in DM supplemented with one of the following: 1% starch and 0.5 mg ml−1 amylase (SA); 1% glucose (G); 0.5 mg ml−1 amylase (A); 1% starch (S); 1% maltose (M2); 1% maltotriose (M3); 1% maltotetraose (M4); 1% maltopentaose (M5); 1% maltohexaose (M6); 1% maltoheptaose (M7); maltoheptaose with 0.5 mg ml−1 amylase (M7A). Total protein precipitated from 1 ml supernatant was loaded onto a sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel, electro-transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane, and the amylase ligand-binding assay was performed. (B) Densitometry analysis of AbpA protein on the same PVDF membranes described above.
